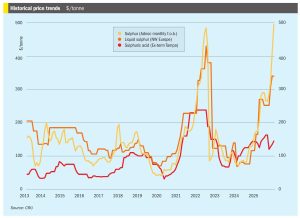
Sulphur ban extended
At the end of December, the Russian government extended its ban on the export of technical sulphur until at least the end of March 2026. The move prolongs the initial restrictions, which were first reported on 4 November and which were set to expire at the end of 2025. The initial ban was widely expected and followed early September drone strikes on the Astrakhan and Orenburg natural-gas plants. The official justification for the extension remains to “stabilise shipments of raw materials to the domestic market” and maintain production volumes for mineral fertilizers, according to the government’s press service Interfax.