
Sulphuric acid recycling
As producers and regulators become increasingly concerned about the ‘circular economy’, there is increasing focus on regenerating waste sulphuric acid for re-use.

As producers and regulators become increasingly concerned about the ‘circular economy’, there is increasing focus on regenerating waste sulphuric acid for re-use.

Hydrocarbon-based production of ammonia carries an unavoidable carbon footprint. But one of the best methods for mitigating that footprint is already here: ultra-low carbon-intensity ammonia production, also known as “blue” ammonia. With blue ammonia production, a typical ammonia plant can sequester or repurpose game-changing volumes of carbon dioxide that would otherwise end up in the atmosphere. To help foster an optimal understanding of the benefits, Ameet Kakoti and Per Juul Dahl of Topsoe A/S provide an overview of the technologies that can help any ammonia operation achieve and maintain sustainable operations – sooner rather than later.

Horisont Energi has the aspiration to develop the most carbon and energy efficient blue ammonia plant in the world, an environmentally friendly plant with a focus on sustainable solutions. This article describes the main features of the Barents Blue Ammonia project, such as 99% carbon capture rate target, a high degree of modularisation, winterisation, infrastructure for ammonia and CO2 management and the provision for future expansion.
Kazakhstan’s oil and condensate output increased by 7% from 1.79 million bbl/d to 1.92 million bbl/d in early June after sour gas reinjection operations resumed at the Kashagan offshore oil and gas development following a recent outage, according to the Kazkah Energy Ministry. Reinjection of sour gas into two wells resumed on 8th June, enabling operator the North Caspian Operating Company (NCOC) to boost oil and condensate production at a large artificial island in Kazakhstan’s Caspian Sea waters. Reinjection was paused on May 20th following the detection of sour gas during routine sampling and a subsequent integrity test. Kashagan normally produces about 300,000 barrels of oil per day. Kazakhstan expects Kashsgan to raise oil production this year to 18.2 million t/a from 12.7 million t/a in 2022.

In 2019 Topsoe launched its ClearView™ technology for WSA and SNOx sulphuric acid plants. This article focuses on the results and learnings from the first implementation of ClearView™ at a new WSA plant at Anglo American Platinum’s Polokwane smelter in South Africa.

The first global review of phosphate rock resources since 2010 has reported that technically recoverable reserves should last for more than 300 years.

CRU, a leader in sulphur industry market analysis, price assessments, consultancy and events, and Abu Dhabi-based UniverSUL Consulting LLC, dedicated to providing unbiased technical expertise in sour hydrocarbon production and sulphur recovery, have announced a formal partnership aimed at enhancing the value of industry events for the sulphur industry.

CRU’s Nitrogen + Syngas conference convened at the Hyatt Regency Barcelona Tower in Barcelona, from March 5th-8th.

BASF says that its high-pressure regenerative CO2 capture technology HiPACT ® , codeveloped by BASF and engineering partner JGC Corporation will be used by INPEX, one of Japan’s largest exploration and production companies, in its Kashiwazaki Clean Hydrogen/Ammonia Project. This is Japan’s first demonstration project for the production of blue hydrogen/ammonia from domestically produced natural gas, the consistent implementation of carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) in domestic depleted gas fields and the use of hydrogen for power generation and ammonia production. The project is funded by the Japanese governmental organization New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
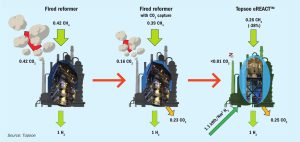
The world’s most common syngas production method remains steam methane reforming, a process which has a substantial CO2 footprint as the necessary reaction heat is supplied by combustion of hydrocarbons. Topsoe’s eREACT™ technology allows for the first-of-its-kind electrification of the traditional SMR process. The reaction heat for eREACT™ is instead generated directly by (renewable) electricity, thereby eliminating the flue gas altogether. Having gone through scale-up from bench scale to industrially relevant pilot scale the technology is now ready for industrial application.