
Urea technology showcase
Toyo Engineering Corporation, Stamicarbon and Saipem showcase their state-of-the-art urea technologies.

Toyo Engineering Corporation, Stamicarbon and Saipem showcase their state-of-the-art urea technologies.

Boron fertilization can improve coffee crop quality and yield. Fabiano Silvestrin of U.S. Borax reviews the evidence.

Brazil is well-positioned to lead the global transition to low-carbon ‘green’ fertilizers, suggests Petter Ostbo, CEO and founder, Atlas Agro.

Supplying nitrate with iodine has been shown to deliver blueberry yield and quality improvements, says Katja Hora, SQM’s Research Manager.

AGI (Ag Growth International) recently installed its first vertical fertilizer blending tower system in Brazil for Mosaic.
In this CRU Insight, Humphrey Knight assesses the key market factors driving high SOP pricing.
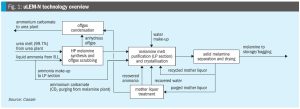
CASALE has expanded its melamine technololgy portfolio with uLEM-N, a market-driven technology development, which retains the industrial proven high-pressure synthesis section and urea-based offgas scrubbing of the LEM® and uLEM® technologies, and uses an innovative purification section which enhances the process reliability while minimising the energy consumption.
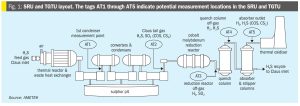
Maximising sulphur recovery in a modified Claus SRU/TGTU requires controlling and monitoring COS and CS2. Leveraging decades of monitoring experience, AMETEK Process Instruments discusses the formation, impact and monitoring of COS and CS2.

The Sulphur Institute celebrates its 65th anniversary this year. In this article the organisation describes its lasting legacy and global impact.

Venkat Pattabathula reports on the American Institute of Chemical Engineers’ (AIChE) Safety in Ammonia Plants and Related Facilities Symposium, held from September 7–11th 2025, in Atlanta, Georgia, USA.