
Transporting sulphur safely
Sulphur is a relatively safe and inert solid. However, it has a number of unique physical and chemical properties which can give rise to hazards, particularly during transport and handling.

Sulphur is a relatively safe and inert solid. However, it has a number of unique physical and chemical properties which can give rise to hazards, particularly during transport and handling.

The refurbishment and modernisation of fertilizer plants offers the opportunity to reduce operating costs, raise production capacity, improve energy efficiency and cut emissions.

The trend for multicomponent analysis of emissions from sulphur recovery units is becoming more widespread. David Inward of Sick reports on a recent field trial to test the suitability of a hot extractive infra-red analyser for this application. In addition to reliably measuring and reporting emissions to air, the analyser is also capable of contributing to reducing overall tail gas emissions by supporting enhanced optimisation of the thermal oxidiser.

The COP-26 summit in Glasgow last year signed into force new rules on carbon emissions trading which may gradually start to see carbon pricing spread worldwide, with knock-on effects on emissions intensive industries like ammonia and methanol.
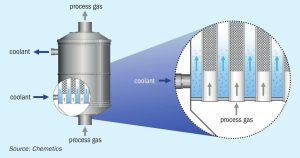
With climate change looming there is an increased focus on reducing the environmental footprint of the production of fertilizers. The use of renewable energy/green hydrogen is one way to make the fertilizer industry more environmentally sustainable. In this article, Rene Dijkstra of Chemetics introduces the Green Fertilizer Complex. This practical solution integrates an oxygen-based sulphuric acid plant using the Chemetics’ patented CORE-SO2™ process with a green hydrogen and ammonia facility to deliver low cost, low emission, and carbon-free phosphate (MAP/DAP) and/or sulphate (AMS) based ammonia fertilizers.

State-of-the art technologies offered by thyssenkrupp, Casale and Stamicarbon are helping make nitrates production more secure and sustainable.

Catalytic converters are the heart and hub of sulphuric acid plants. Converter replacement of equipment that has come to the end of its life is an opportunity to make improvements to the performance, productivity, reliability, durability and plant emissions. NORAM discusses design and project execution considerations for SO2 catalytic converter replacement and Chemetics considers the challenges and opportunities of converter retrofits.

Improvements to nutrient use efficiency (NUE), particularly for nitrogen, can deliver dual environmental and economic benefits. We report on recent developments in nitrogen management and global progress on NUE.
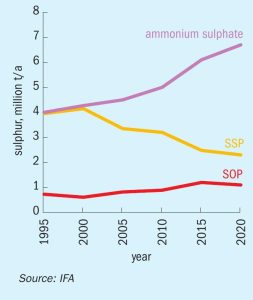
Sulphur is becoming an increasingly important crop nutrient, due to a combination of lower airborne sulphur emissions, the increasing prevalence of high analysis fertilizers, and higher cropping intensities.

Considering the current shift to produce biofuels instead of conventional oil products, M. van Son of Comprimo discusses the impact that this may have on the ability to process the sour water acid gas streams produced in existing or new sour water strippers.