Market Outlook
• The short term outlook appears balanced for the most part, although more bullish participants seem to be holding sway over market sentiment.

• The short term outlook appears balanced for the most part, although more bullish participants seem to be holding sway over market sentiment.

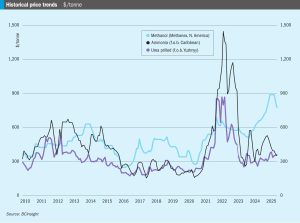
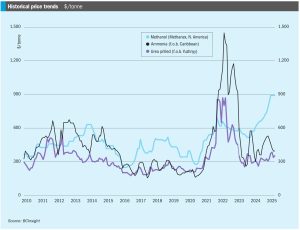
Ju ne saw fertilizer markets – urea markets in particular – thrown into chaos by the widening of hostilities in the Middle East. Israel’s and then the United States’ strikes on Iranian nuclear facilities and the retaliatory attacks on Israel and Qatar for a while held out the potential for the conflict to widen, perhaps even leading to attempts to close the straits of Hormuz at the entrance to the Gulf, something not seen since the ‘tanker war’ of the 1980s when Iraq tried to cripple Iran’s oil exports during the eight year Iran-Iraq War.

The Iran-Israel conflict in mid-June placed the urea market on edge prior to a ceasefire announcement.
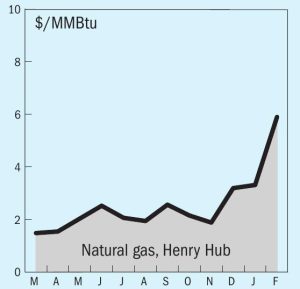
Price trends and the market outlook, 19th June 2025

Alleima's SAF 2906 high-performance stainless steel - advanced material for urea
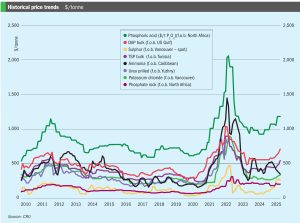
Price trends and the market outlook, 10th April 2025

It is with great sadness that we report the death of Dr. Umberto Zardi, who passed away on March 17th 2025 at his home in Breganzona, Lugano, Switzerland. Dr Zardi was an innovator in the nitrogen industry and for many years the president and driving force behind Ammonia Casale, now simply Casale SA, becoming responsible for its revival and transformation into the global engineering and technology giant that it is today.

Dr M.P. Sukumaran Nair, Director of the Centre for Green Technology & Management, Cochin, India and former Secretary to the Chief Minister of Kerala discusses the challenges facing India’s agriculture and fertilizer industry.
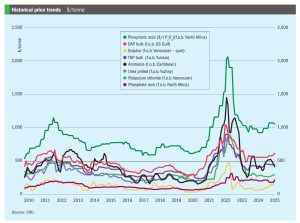
• Continuing oversupply means that ammonia prices should continue to come under pressure moving into 2H April, though it remains to be seen just how much further values in Asia can decline before producers begin to shutter output.
In mid-April, Ammonia prices both east and west of Suez remained firmly oriented to the downside, with supply still heavily outweighing demand and suppliers scrambling to place excess tonnage. Bearish market sentiment was exemplified by a Trammo sale to OCP at $415/t c.fr Morocco, $20/t short of Tampa’s c.fr settlement for April and around $44/t down on February.