
Australia’s acid conundrum
The progressive closure of smelter capacity in Australia poses potential problems for acid consumers across the country.

The progressive closure of smelter capacity in Australia poses potential problems for acid consumers across the country.
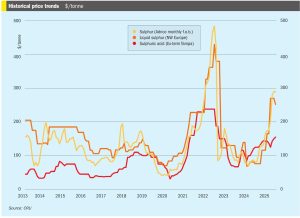
• Global sulphur prices are expected to experience decreases over the next few weeks. Buyers in Asia report that they are covered for contracted supply throughout July, and domestic prices in China are likely to decrease further, putting downward pressure on sulphur prices.

The end of June saw declines in sulphur prices in many regions amid subdued global demand across regions. Most import markets are sufficiently covered through July at least, resulting in limited activity while supply increases. These conditions have exerted downward pressure on prices as bearish sentiment spread across regions.

Titanium dioxide is one of the major chemical uses for sulphuric acid outside of phosphate and metals processing, and sulphate route plants remain concentrated in China.

Indonesia has become the epicentre of the world nickel industry, and is now seeking to raise royalty rates to capture more value from this. Will this impact upon the continuing expansion of HPAL capacity there?

While the US tariff situation remains subject to considerable uncertainty, there has already been an impact on short term trade flows, as well as investment decisions.

The Sulphur Institute (TSI) held its World Sulphur Symposium in Florence from April 8th-10th.

The Middle East remains the world’s largest regional exporter of sulphur, with additional capacity continuing to come from both refineries and particularly sour gas processing.
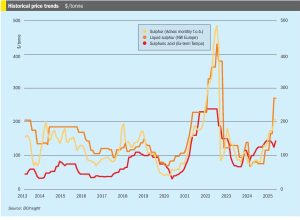
• Global sulphur prices are expected to stay relatively stable as purchases in Asia slow down due to the closing of the purchasing window for the Chinese spring fertilizer application season.
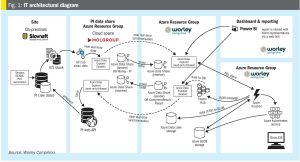
Together with Slovnaft, Worley Comprimo has developed a near real-time monitoring dashboard using data sharing via the Cloud. Using a two-year data set containing minute average data, trends and insights were used to optimise performance. This paper describes the main learnings and improvements with respect to energy optimisation, which supports sustainability targets for Slovnaft.