
The Sulphur Institute at 65
The Sulphur Institute celebrates its 65th anniversary this year. In this article the organisation describes its lasting legacy and global impact.

The Sulphur Institute celebrates its 65th anniversary this year. In this article the organisation describes its lasting legacy and global impact.
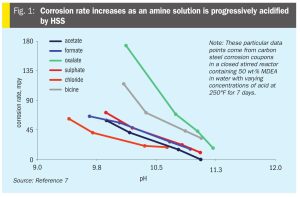
Joel Cantrell of Bryan Research & Engineering and Clay Jones of INEOS GAS/SPEC re-evaluate the historical practice of intentionally adding strong base such as caustic (NaOH) to amine with the purpose of improving performance and reducing corrosion by “neutralising” heat stable amine salts (HSAS) which have accumulated in the amine.

Platinum-promoted honeycomb catalyst bricks offer function as total oxidation catalysts that convert all oxidisable species under appropriate temperature and oxygen conditions. P&P Industries presents a case for a H2S-rich gas stream – relevant to the fibre industry, Claus offgas treatment, and other chemical sectors.

A full sulphur pit turnaround and rehabilitation is typically a once in a lifetime experience for refinery personnel. Specialists in sulphur pit turnarounds, Gavin Palmer of Brindley Engineering, Tom Kline and Bob Hall of Structural Technologies have compiled a database based on multiple sulphur pit turnarounds to identify typical deficiencies in mechanical systems, along with improvements to enhance operability, restore functionality and meet all codes/standards and best practices.

Continuous monitoring of sulphur recovery units (SRUs) has proven to be an excellent tool for energy optimisation and emissions reduction, yielding financial incentives in the form of CO2 credits and sustainability. Even in markets with limited CO2 credits, significant economic benefits can still be realised through reduction in utility consumption, as demonstrated by a recent collaboration between Worley Comprimo and PRefChem in Malaysia.

Freeport Indonesia may be forced to suspend operations at its Manyar smelter at the end of October due to a lack of copper concentrate, according to local press reports. The news follows the mudslide at the Grasberg mine in September, which killed seven workers. Grasberg, which represents almost 3% of global copper mine production, has halted production and Freeport says that it may not return to pre-accident operating rates until 2027. Stocks of copper concentrate at Grasberg were estimated to be only sufficient to operate the Manyar smelter until the end of October. The $3.7 billion Manyar smelter only resumed operations in May after a fire broke out in October last year, damaging the plant.

Sultech Global Innovation Corp., a Canadian agricultural technology company, has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with ADNOC Sour Gas for its micronised elemental sulphur technology. Under the MoU, the companies will conduct a feasibility study and pilot production program to establish the UAE’s first commercial micronised sulphur manufacturing facility. The initiative will integrate Sultech’s patented micronisation process within ADNOC’s sulphur granulation at the Shah Gas Plant, the world’s largest ultra-sour gas operation.

Metso has completed the expansion of its service centre in Antofagasta, Chile, adding an additional 1,200 m² of operational capacity, totalling 4,800 m² of technical workspace. Strategically located in the La Negra industrial district, at the heart of northern Chile’s mining area, the service centre has tripled its technical-commercial agreements in recent years, becoming a key strategic partner for major mining companies in the country. Following the expansion, the centre can now repair and refurbish large-scale equipment including HRC™ and high pressure grinding roll units, Vertimill® grinding technology, and mills for mining customers. It also supports beneficiation and dewatering technologies, such as filter plate pack service offerings. In addition, the centre provides service capabilities for mining crushers, grinding mills, screens, and car dumpers.

ADNOC has received bids for its Ruwais Sulphur Terminal expansion. The project aims to expand the existing sulphur handling terminal facilities, SHT-1 and SHT-2, located in Ruwais, Abu Dhabi. The purpose of the expansion is to increase the capacity of the Ruwais sulphur handling terminal to accommodate an additional 10,600 t/d of liquid sulphur from the Hail and Ghasha offshore sour gas field development.

Austrlai’s Northern Territories Government has approved a mining licence for Verdant Minerals’ Ammaroo phosphate project. The approval follows the granting of two mineral leases in March and represents a critical step towards construction and mining operations at one of the world’s largest phosphate resources. Verdant estimates the value of production over the life of the mine to exceed $15 billion. Verdant says that securing the mining licence puts the project firmly on track to reach a final investment decision and commence construction as early as mid-2027. Located 200 kilometres south-east of Tennant Creek, the Ammaroo phosphate deposit contains more than one billion tonnes of phosphate ore.