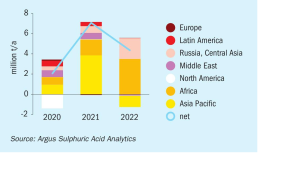
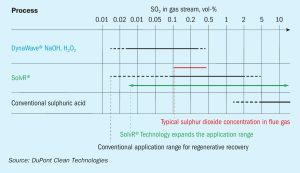
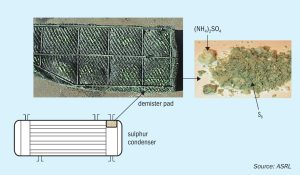
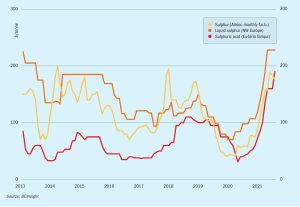
Sulphur Industry News Roundup
India’s power and renewable energy minister RK Singh has placed draft plans before the cabinet for the country’s refining and fertilizer sectors to switch to renewable ‘green’ hydrogen feeds. Other energy intensive sectors such as steel and transport are likely to follow. The policy suggests that refiners must have 10% of their hydrogen consumption generated from renewable electricity by the end of financial year 2023-24, rising to 25% by 2030. The comparable figures for ammonia/urea production are 5% and 20%, respectively. India is pursuing some of the world’s most ambitious renewable energy targets of 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by the end of 2022 and 450 GW by 2030.