Round up days 2 and 3 CRU Nitrogen+Syngas ExpoConference
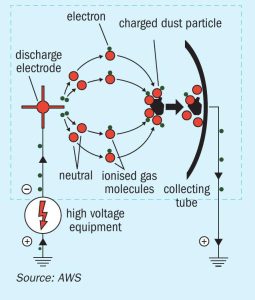
Days 2 and 3 of the CRU’s 38th Nitrogen+Syngas 2025 Expoconference turned to the technical sessions, organised in three parallel streams covering: green ammonia technology, nitric acid and ammonium nitrate, plant operations and reliability, urea technology, digitalisation, carbon capture, emissions reduction and sustainable fertilizer production, and fertilizer finishing.