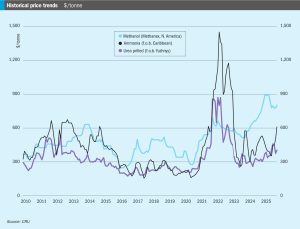
Prices in sulphur markets have been climbing rapidly for several weeks now due to short supply, reaching their highest levels for early two and a half years, since July 2022. A major cause has been widening Ukrainian drone and missile strikes against Russian oil and gas facilities. In particular, drone strikes in September on the Astrakhan and Orenburg natural gas plants led to Russian sulphur exports being cut drastically, first from around 400,000 tonnes per month to only 100,000 tonnes in October, and then to zero from the 1st of November, as Russia implemented a ban on exports of sulphur used in fertilizer production which was projected to last at least until December 31st. “This decision will stabilise shipments of raw materials to the domestic market to maintain current mineral fertilizer production volumes and ensure the country’s food security,” the government’s press service reported. The restriction applies to the export of liquid, granulated, and lump sulphur. It remains to be seen whether exports of Kazakh material from Ust Luga will be affected, but some Kazakh sulphur is now being sold via Iran.