Nitrogen+Syngas 399 Jan-Feb 2026
27 January 2026
Price Trends
Price Trends
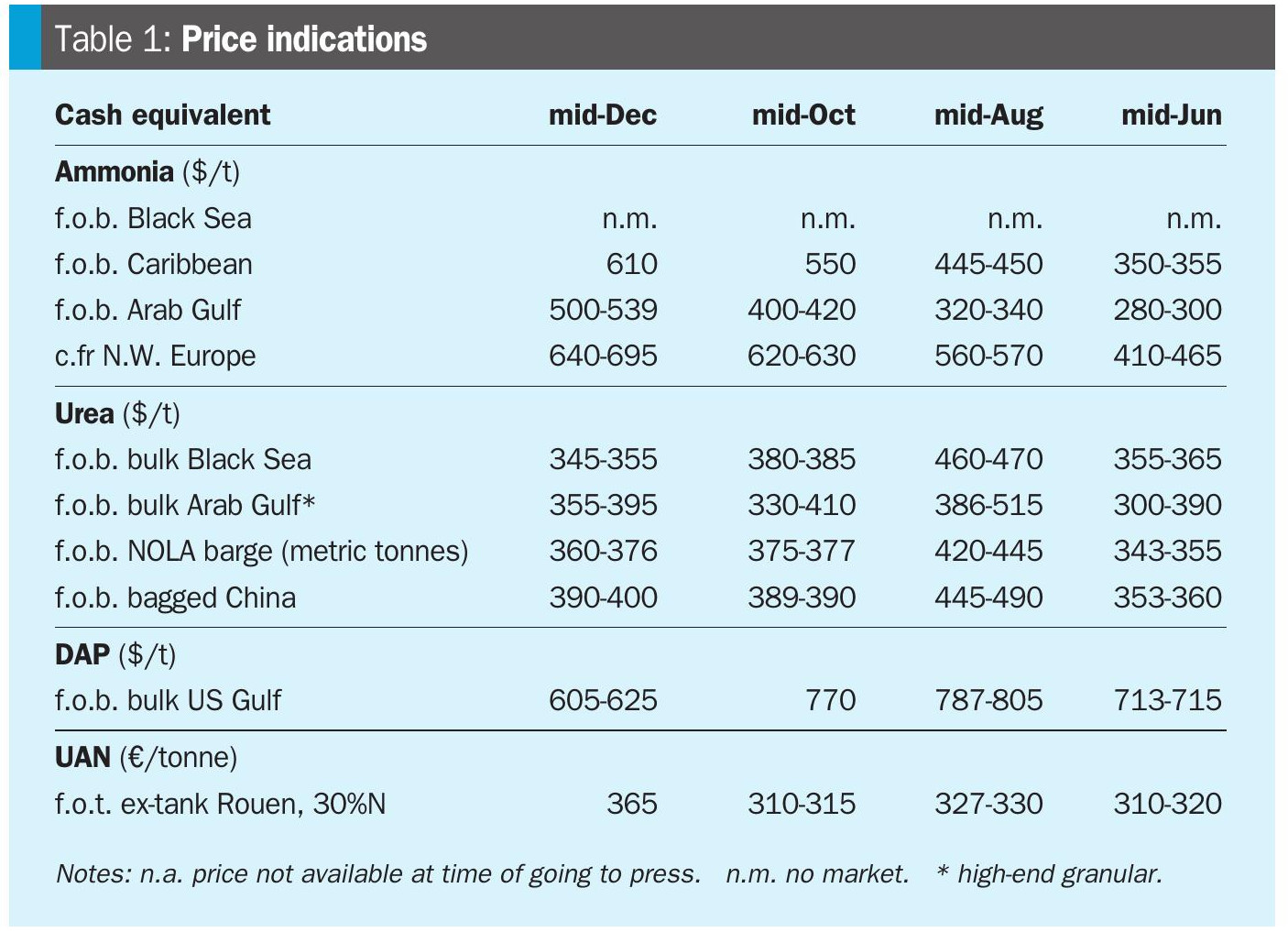
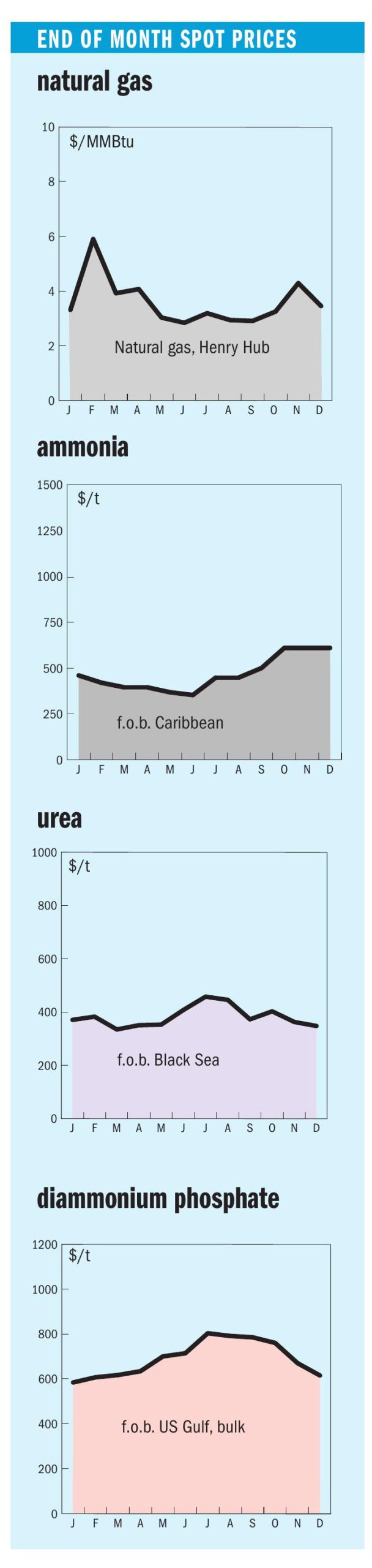
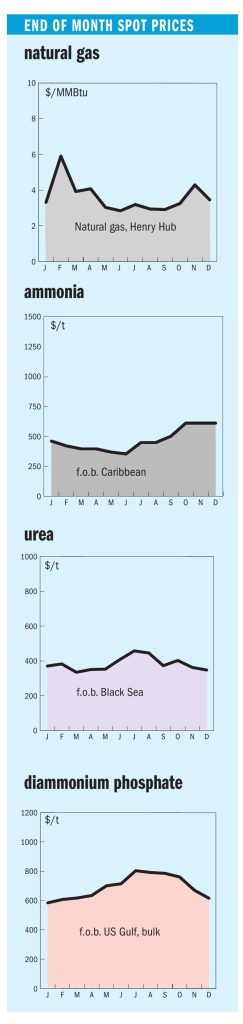
Ammonia values in the Middle East, Far East and Southeast Asia edged higher at the start of January, while other major benchmarks were largely unchanged amid a subdued market. Conditions at the start of the year mirror late2025, with prices supported by persistent supply tightness from the continued absence of Ma’aden’s MPC facility, which removes an estimated 300– 400,000 tonnes from the market. The unit is expected to return in mid-to-late January.
The key development remains the implementation of CBAM in northwest Europe, where activity has slowed. Default emissions values issued by the European Commission in late December have effectively priced US tonnes out of the market, forcing producers to verify carbon intensity to stay competitive.
Indian prices extended their upward trajectory, with delivered values reaching $550/t c.fr after confirmation of cargoes secured from Southeast Asia. Firm c.fr prices were supported by higher f.o.b. levels, though sentiment turned cautious on expectations of Ma’aden’s restart and the potential for additional merchant supply should Indian producers bring forward shutdowns amid elevated feedstock costs. Supply in the Middle East remains constrained, with both Ma’aden’s MPC plant and Sabic’s Al Jubail facility still offline. In Algeria, one new pot sale for 10,000 tonnes at $600/t f.o.b. was reported.
In the US Gulf, GCA’s January loadings continued to build, reaching approximately 97,400 tonnes. In Italy, Yara’s Ferrera plant remains offline, prompting Ravenna to import ammonia; so far only one vessel carrying Algerian tonnes has arrived at Ravenna.
Global urea market action was largely confined to east of Suez, where India’s National Fertilizers Limited (NFL) closed a fresh purchase enquiry on 2nd January. Having initially sought 1.5 million tonnes for shipment by 20 February, NFL received offers totalling just over 3.62 million tonnes. The lowest offers emerged from Koch, and counters to remaining participants – after several deadline extensions – saw acceptances eventually reach 976,750 tonnes.
Across the Indian Ocean in the Middle East, prices gained support following India’s developments. Netbacks on the lowest offers were in the low$410s/t f.o.b., though Qatar-Energy concluded February business in the high$410s f.o.b., and was reported to have sold prills via tender in the mid$390s/t f.o.b. In Iran, with just one of seven producers running, prices inched up: the official weekly price was initially $390/t f.o.b., while the sole remaining producer, Pardis, subsequently sold granular material at $397/t f.o.b.; further business is likely above $400/t f.o.b. Seasonal gas curtailments are expected to last until at least February.
West of Suez, Mopco reported granular sales in the $450–455/t f.o.b. range in Egypt, though destinations for the cargoes were not disclosed. Any supply to Europe would, in theory, be subject to CBAM, which came into effect on 1 January. Signals from European officials that CBAM could potentially be halted have cast doubt on whether the mechanism will survive the year, despite assurances from other EU officials that it remains in place for now.