
IFA 2025 Annual Conference report
Selected highlights of the International Fertilizer Association’s Annual Conference in Monaco in mid-May.

Selected highlights of the International Fertilizer Association’s Annual Conference in Monaco in mid-May.
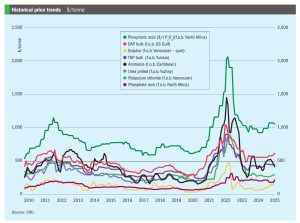
Price trends and the market outlook, 10th April 2025

While the US tariff situation remains subject to considerable uncertainty, there has already been an impact on short term trade flows, as well as investment decisions.
Sulphur markets have been on a tear over the past few months, driven by strong demand in Asia, with buyers primarily sourcing from the Middle East and Canada through late 2024 and into the early months of 2025. Steady buying from Indonesia and China, the two largest importers of sulphur, appears to have supported the market, in China’s case mainly for phosphate production as well as a variety of industrial processes, and in Indonesia’s case to feed the high pressure acid leach (HPAL) plants that are producing nickel for the battery and stainless steel industries. Prices saw a notable rally following the Chinese Lunar New Year celebrations. Nevertheless, this momentum finally began to shift as April began ago as the pace of price increases in Asia started to slow. As the spring fertilizer application season in China draws to a close, domestic prices began to drop, reaching the equivalent of a delivered price of around $272/t c.fr. As well as the narrowing window for spring application of phosphates, the decline was also driven by weakening demand amid uncertainty over tariffs and export restrictions. In southern China, phosphate producers continue to purchase import cargoes. A major phosphate producer in southwest China has been reported as having bought mainstream material at a price of $303/t c.fr, according to local market sources. Total sulphur port inventories in China had declined by 22,000 tonnes to 1.86 million tonnes by 16 April 2025. The volume at Yangtze River ports increased to 825,000 tonnes, while the port inventory at Dafeng decreased to 400,000 tonnes.
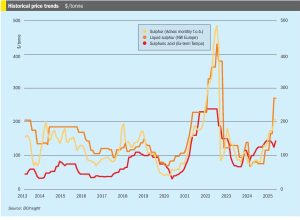
• Global sulphur prices are expected to stay relatively stable as purchases in Asia slow down due to the closing of the purchasing window for the Chinese spring fertilizer application season.

Indonesia is increasing the royalty rates that the government takes on metals mined within the country. The Indonesian government has proposed a tiered royalty structure on nickel ore sales, ranging between 14–19%, depending on the prevailing nickel price. This would replace the current flat rate of 10%. A 14% rate would apply when nickel prices are below $18,000 /t, increasing progressively to 19% for LME prices above $31,000 /t. The royalty is calculated based on revenue from nickel ore sales.
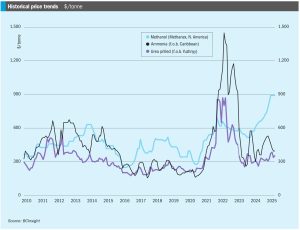
• Continuing oversupply means that ammonia prices should continue to come under pressure moving into 2H April, though it remains to be seen just how much further values in Asia can decline before producers begin to shutter output.
In mid-April, Ammonia prices both east and west of Suez remained firmly oriented to the downside, with supply still heavily outweighing demand and suppliers scrambling to place excess tonnage. Bearish market sentiment was exemplified by a Trammo sale to OCP at $415/t c.fr Morocco, $20/t short of Tampa’s c.fr settlement for April and around $44/t down on February.

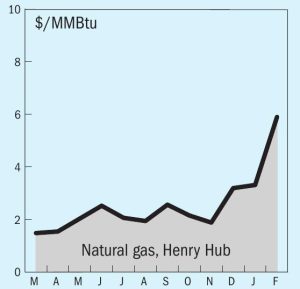
Global gas demand has returned to growth after the supply shock of 2022-23, but geopolitical tensions and short supply in LNG markets.

P r esident Trump’s flurry of activity in his first month of office has not only upended the global political order that has existed, more or less, since the US rearranged it to its satisfaction in 1945, but has also had a seismic impact on world trade. How the various strands of US policy will play out remains highly uncertain, but some clear trends are beginning to emerge.