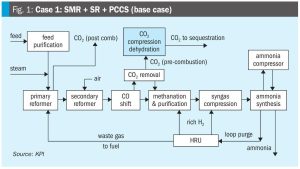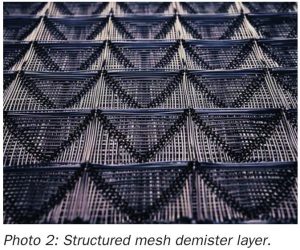
Defined, designed, delivered, diagnosed
Begg Cousland Envirotec reviews different mist eliminator types and some of the operational problems encountered which can be managed by correct installation, targeted cleaning or replacement, and selecting appropriate corrosion-resistant materials.