
Morocco’s new acid capacity
Morocco’s OCP is continuing to expand its phosphate fertilizer production capacity. This includes the construction of new sulphur-burning acid capacity to support phosphate production and provide carbon-free power.

Morocco’s OCP is continuing to expand its phosphate fertilizer production capacity. This includes the construction of new sulphur-burning acid capacity to support phosphate production and provide carbon-free power.

Sulphur Experts outline the steps required to determine optimised SRU incinerator operating conditions. Although a proper determination of the ideal SRU incinerator operating conditions for any given facility is complicated by a combination of inconsistent permitting standards and poor understanding of the role of the SRU incinerator, the payoff for incinerator optimisation is a significant decrease in natural gas usage with corresponding savings in operating costs, a decrease in CO2 emissions, and a simultaneous reduction in NOx and SO3 emissions.

We review potash mining and mineral processing methods. Advances in equipment technology and major project investments are highlighted.

Christof Group SBN presents groundbreaking sensor technology for accurate and reliable continuous monitoring of individual heat exchanger tube wall thickness in high pressure, high temperature industrial conditions.
Catalyst development for nitric acid plants is strongly dependent on operating pressures and nitrogen loading levels. Johnson Matthey reviews some of the key catalyst design principles, emphasising the critical role of operating pressure in catalyst selection and highlighting the innovative contributions of Johnson Matthey in advancing catalyst technology for ultra-high-pressure ammonia oxidation in nitric acid plants.
MECS, Inc. (MECS) has developed a new impaction-based mist eliminator called Brink® Prime Impact™ , which offers equivalent or improved efficiency at higher throughput and the same pressure drop as traditional impaction beds, resulting in the ability to debottleneck existing inter-pass absorption towers and final absorption towers in sulphuric acid plants or design new or replacement towers with smaller diameters, thus reducing investment cost.

This case study reports on the successful collaboration of two experienced partner companies to replace the problematic upper part of a co-current flow quench tower in a spent acid plant and shows the benefits of using resistant, pre-lined workshop fabricated equipment.
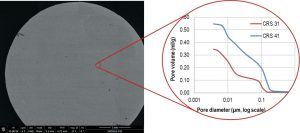
Axens has developed a new titania-based catalyst named CRS 41, which has a much larger porosity than its renowned predecessor, CRS 31 catalyst. Thanks to an improved catalyst manufacturing process and a new recipe, the porosity of CRS 41 has been increased while preserving the mechanical resistance for loading, allowing customers to optimise their capex by either reducing the Claus reactor size or loading volume of TiO2 catalyst.
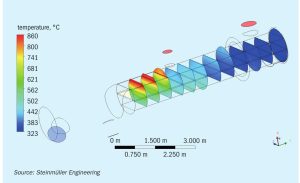
Steinmüller Engineering shares its experiences of applying CFD to re-design the waste heat boiler downstream of the secondary reformer to successfully achieve the desired uniform cross flow across the tube bundle.

PT Petrokimia Gresik detail an inventive redesign of their economiser, a critical component in sulphuric acid production, focusing on energy efficiency, decarbonisation, process optimisation, and equipment durability.