Cobalt-molybdenum catalyst activation in low temperature TGUs
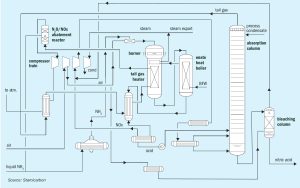
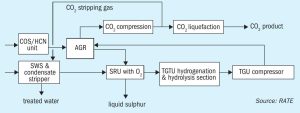
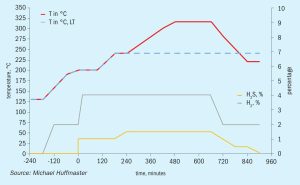
In the final part of this two-part article, Michael Huffmaster , Consultant, presents case study results using a discrete reactor model incorporating heat, mass transfer, and activation reaction kinetics to assess the impacts of these variables on in-bed temperature profile and activation effectiveness. Tailoring gas rate, composition, and temperature progression can achieve in-bed exotherms which improve CoMo catalyst activation effectiveness for low temperature tail gas units.