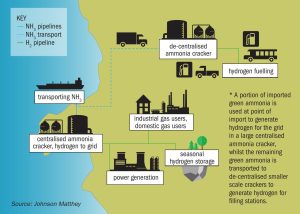
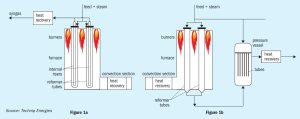
Barents Blue Ammonia project
Horisont Energi has the aspiration to develop the most carbon and energy efficient blue ammonia plant in the world, an environmentally friendly plant with a focus on sustainable solutions. This article describes the main features of the Barents Blue Ammonia project, such as 99% carbon capture rate target, a high degree of modularisation, winterisation, infrastructure for ammonia and CO2 management and the provision for future expansion.