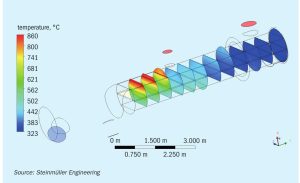
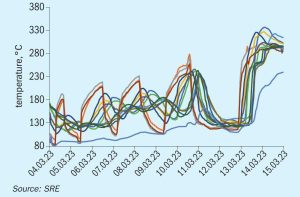
An ideal reactor for green methanol
As the production of renewable methanol continues to scale up, it will provide a long term, carbon-neutral energy solution to different transport sectors. However, the optimum design parameters for green methanol plants are substantially different to natural gas-based methanol plants and pose new challenges to the methanol loop designer. Johnson Matthey discusses the challenges and presents the benefits of the tube cooled converter for e-methanol production.