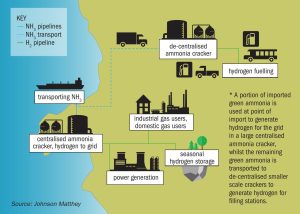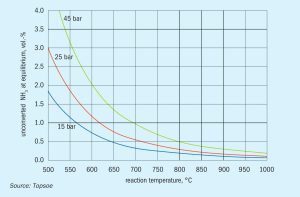
Efficient and proven ammonia cracking at scale
Large-scale ammonia cracking for conversion of ammonia to hydrogen is a proven technology with decades of industrial experience. Topsoe shares its experience within ammonia cracking and presents an improved and highly energy-efficient (96%) ammonia cracking technology, H2Retake™ , developed based on Topsoe’s proven technology and industrial experience.