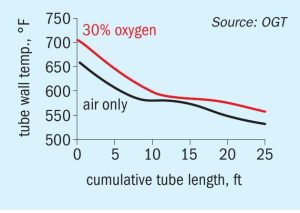
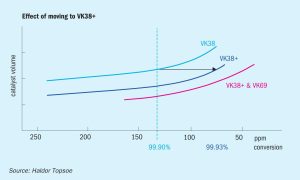
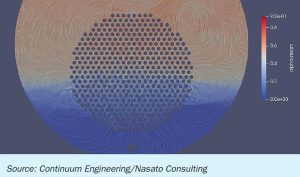
Johnson Matthey (JM) has secured a multiple licence for China’s Ningxia Baofeng Energy Group’s latest project to develop five of the largest single train methanol plants in the world. Located at Baofeng’s Ordos City complex in Inner Mongolia, the five plants each have a planned capacity 7,200 t/d. Under the agreement Johnson Matthey will be the licensor of all five plants and supplier of associated engineering, technical review, commissioning assistance, and catalyst. The plants will take synthesis gas as a feed and use JM radial steam raising converters in a patented series loop. Within the design, there is potential for 1-2% more feedstock efficiency over the life of the catalyst. Thanks to JM’s methanol loop synthesis technology, the plants will provide enhanced energy savings along with low OPEX, CAPEX and emissions. When complete, the plants will represent JM’s 13th operating license in China for a mega-scale plant (>5,500 t/d) and the fourth JM methanol design licensed by Ningxia Baofeng Energy.