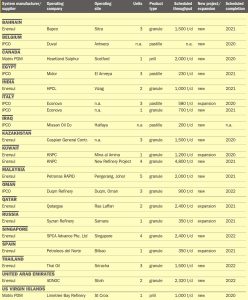
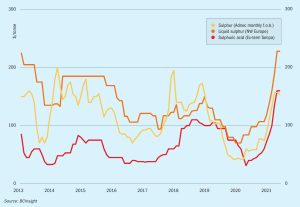
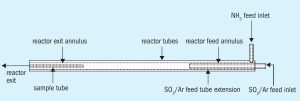
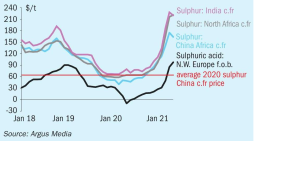
Sulphuric Acid News Roundup
Production has begun at Ivanhoe Mines’ Kakula copper mine in the DRC. The company says that total production for this year is expected to be 80-95,000 t/a of copper in concentrate, with a phase two expansion to 400,000 t/a due to be completed by Q2 2022. Ivanhoe is working with China’s Zijin Mining on the development plan for phases 2 and 3 of the mine, as well as a feasibility study for the Kipushi zinc mine further to the east. Both projects lie close to the DRC’s southern border, with Angola and Zambia respectively. Phase 3 of Kamoa will lift capacity to an anticipated 600-800,000 t/a of copper in concentrate, making it the second largest copper mine in the world after Escondida in Chile. Canadian-based Ivanhoe expects to be digging 3.8 million t/a of ore at Kakula with 6% copper content in Phase 1.