Sulphur Index 2022
A complete listing of all articles and news items that appeared in Sulphur magazine during 2022.
A complete listing of all articles and news items that appeared in Sulphur magazine during 2022.
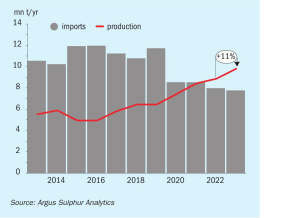
Meena Chauhan, Head of Sulphur and Sulphuric Acid Research, Argus Media, assesses price trends and the market outlook for sulphur.
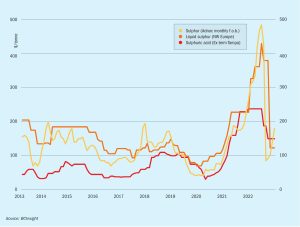
Processed phosphates pricing will be a major influence in the coming months. A gap remains between historical levels of sulphur and DAP pricing that points to the potential for sulphur prices to recover to higher levels during 2023.
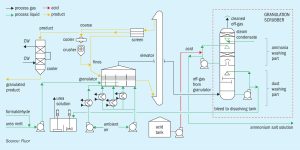
Fluor demonstrates how SRU/TGTU plants within sour gas facilities can facilitate the capture of CO2 and generate H2 by implementing advanced sulphur recovery technologies.

It has long been known that sulphur dioxide aerosols can reflect sunlight back into space. On a large scale, this has tended to come from volcanic eruptions. The explosion of the island of Krakatoa in 1815 led to the following year, 1816, becoming known in Europe as ‘the year without a summer’. More recently, it is estimated that the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in 1991, the second largest eruption of the 20th century, sent around 18 million tonnes of SO2 into the stratosphere. Temperatures in the troposphere – the atmospheric layer closest to the earth – dropped by about 0.5°C as a result for about two years afterwards.

When candle filter mist eliminators installed in the absorption towers in sulphuric acid plants are not sufficiently wet, problems can occur such as free SO3 at the stack, NOx issues and emission non-compliance. Begg Cousland Envirotec discusses how these problems can be overcome by the installation of an annular wetting ring solution.

Industry turnover is a reality, and keeping new employees informed of hydrogen safety procedures in sulphuric acid plants is key to keeping plants fully operational and incident free. Elessent Clean Technologies discusses the steps facilities need to take to prevent hydrogen incidents.

Last year saw global trade in all commodities have to take into account the potential loss of supply from Russia, a key exporter of many commodities. Sulphur was no exception, with prices swinging wildly across the year.

Lithium miner Ioneer Ltd has signed a non-binding Memorandum of Understanding with Shell Canada Energy for the supply of sulphur to Ioneer for its Rhyolite Ridge lithium-boron project in Esmeralda County, Nevada. Ionner said in a statement that “securing the supply of key reagents for ore processing is an important step along the critical pathway to developing the Rhyolite Ridge project”. Under the memorandum, Ioneer will purchase up to 500,000 t/a of high-quality sulphur from Shell, which would fulfil the estimated annual sulphur requirement for the Project.

Ben van Beurden ended his tenure as Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Shell and was replaced by Wael Sawan on January 1st, 2023. Van Beurden will continue working as adviser to the Board until June 30, 2023, after which he will leave the group.