Sulphur 409 Nov-Dec 2023
30 November 2023
Sulphur 409 Nov-Dec 2023

30 November 2023

CRU’s annual Sulphur+Sulphuric Acid Expoconference was held from November 3rd to 5th, at The Woodlands, Texas.

The deficit in the sulphur market has led to a new focus on melting down and selling stockpiles of sulphur around the world. From Kazakhstan to Canada, stocks of sulphur have been shrinking.
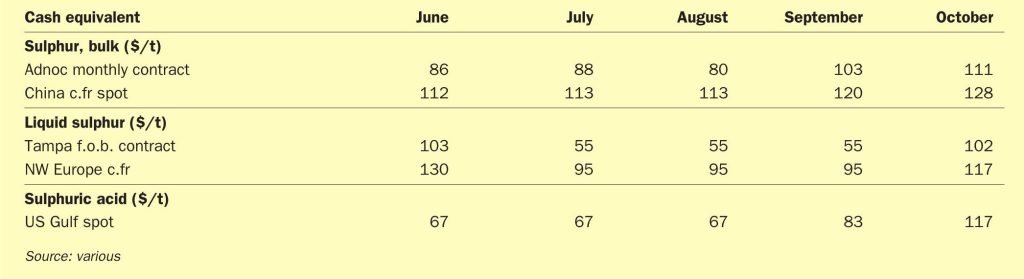
The global sulphur market’s bullish momentum from late 2025 has firmly carried over into the New Year, with prices pushing forward across most key regions despite a slow return to spot trading after the holiday break. With spot prices now past their 2022 highs and testing levels not seen since the 2008 peak, affordability has become the market’s central theme. The market remains divergent, with some buyers forced to accept the rally due to tight supply, while others, particularly in China, are showing clear signs of demand destruction.
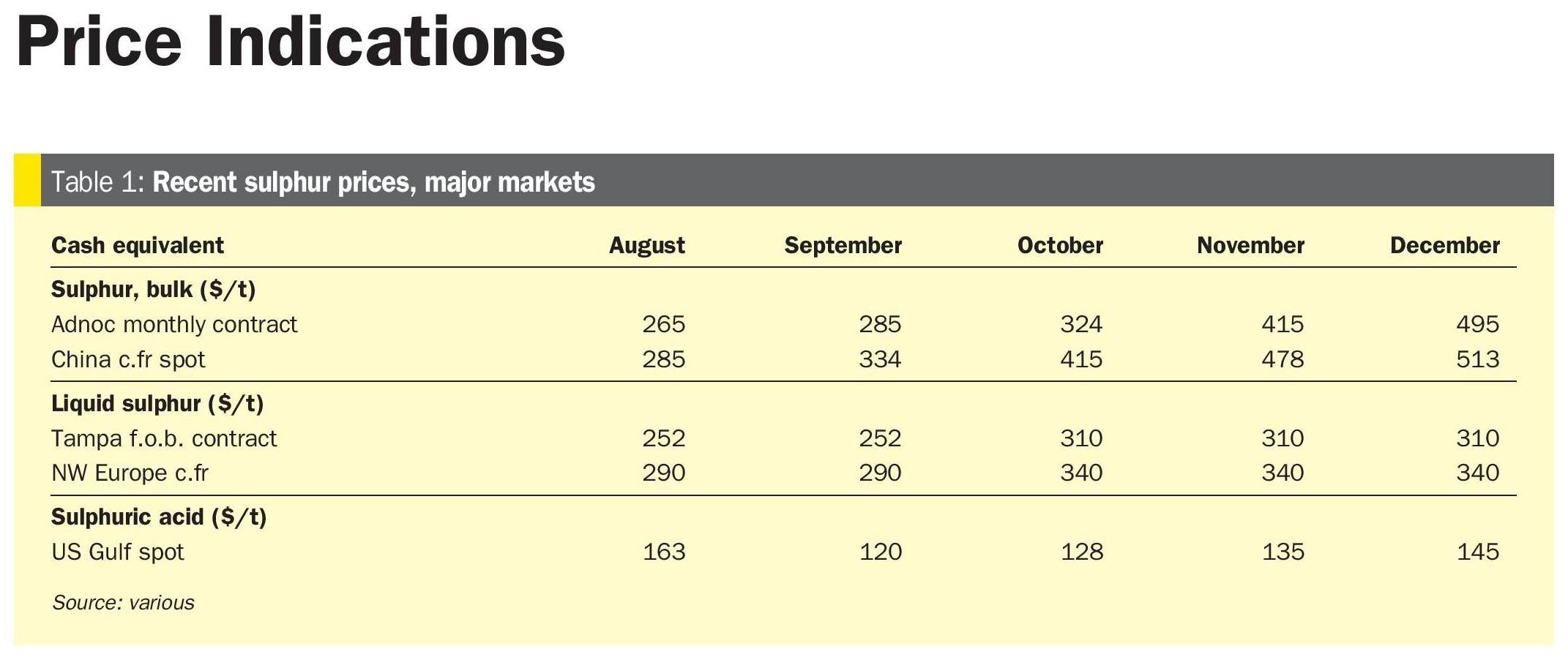
Sulphur prices have risen rapidly in recent months as the market moves into a period of deficit which is likely to last until 2028.

The Chinese ammonium sulphate industry continues to see rapid growth, with exports rising to record levels, against increasing demand coming from Brazil and India.