
Fertilizer Industry News Roundup
BHP has finally given the go ahead for stage one of its Jansen potash mine project in Saskatchewan, Canada.

BHP has finally given the go ahead for stage one of its Jansen potash mine project in Saskatchewan, Canada.

OCI subsidiary Fertiglobe says that it has partnered with the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), to enable the sale by ADNOC of the first cargo of blue ammonia to Itochu in Japan, for use in fertilizer production. Fertiglobe, a 58% − 42% partnership between OCI and ADNOC respectively, will produce the blue ammonia at its Fertil plant at Ruwais in Abu Dhabi for delivery to ADNOC’s customers in Japan. This represent the first production milestone of a planned scale-up of blue ammonia production capabilities in Abu Dhabi, which is expected to include a low-cost debottlenecking program at Fertil. In addition, it was announced in June that Fertiglobe will join ADNOC and sovereign wealth fund ADQ as a partner in a new world-scale 1.0 million t/a blue ammonia project at Ta’Ziz in Ruwais, subject to regulatory approvals. The design contract for this project has been awarded, with a final investment decision expected in 2022 and start-up targeted for 2025. A feasibility study was also agreed in July betweenh the state-owned Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corp. (Jogmec), Inpex and JERA as well as ADNOC to explore the possibility of producing 1.0 million t/a of blue ammonia in Abu Dhabi and transporting it to Japan.

Although the stranded gas boom that led to the construction of the region’s nitrogen capacity in the 1980s-2000s may be largely over, the Middle East remains the largest nitrogen exporting region in the world.
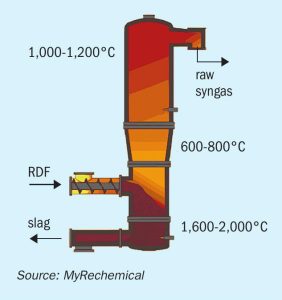
Johnson Matthey and MyRechemical have formed an alliance to commercially develop waste to methanol technology. In this article, two different approaches to waste disposal and chemical production are analysed: a post combustion scenario with waste incineration and hydrogenation of the CO2 recovered from flue gas to produce methanol, and a precombustion approach with waste gasification followed by conversion of synthesis gas into methanol.
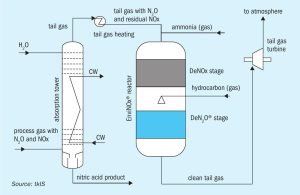
By utilising state-of-the-art technologies, nitric acid and ammonium nitrate producers are able to reduce the environmental impact of their production plants and make a key contribution to climate protection.
India’s power and renewable energy minister RK Singh has placed draft plans before the cabinet for the country’s refining and fertilizer sectors to switch to renewable ‘green’ hydrogen feeds. Other energy intensive sectors such as steel and transport are likely to follow. The policy suggests that refiners must have 10% of their hydrogen consumption generated from renewable electricity by the end of financial year 2023-24, rising to 25% by 2030. The comparable figures for ammonia/urea production are 5% and 20%, respectively. India is pursuing some of the world’s most ambitious renewable energy targets of 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by the end of 2022 and 450 GW by 2030.
During this time of disruption, keeping connected and informed has never been more important. While the in-person events the industry usually relies on are not possible, CRU’s virtual Sustainable Fertilizer Production Technology Forum, 20-23 September, offers exceptional information sharing and networking opportunities.

Plans to decarbonise power production and shipping are leading to increasing interest in using ammonia as a fuel, but technical and economic barriers still remain to be overcome.

To comply with stricter stack emission obligations, industries are required to recover more heat from flue gas and to clean it before it can be discharged into the atmosphere. J. Kitzhofer of APEX Group discusses the challenges and limitations of the majority of current heat recovery systems and reports on a new family of acid resistant tubular and plate-type heat exchangers developed by APEX Group that overcomes these problems. The new heat exchangers are resistant to dew point corrosion. The heat transfer elements are constructed from an acid resistant polymer composite with high thermal conductivity, allowing the design of new trouble-free heat recovery systems and the upgrade of existing systems to meet heat recovery and stack emission targets.

Metal dusting corrosion damage on steam reformers is no longer a major issue in modern methane steam reformer units. Nevertheless, failures related to metal dusting corrosion attack still take place in some specific designs and configurations that are more prone to experience this damage. Poor maintenance or deterioration of insulation components on transition areas might expose metallic surfaces to metal dusting attack. In this article, Dr P. Cardín and P. Imízcoz of Schmidt+Clemens Group describe different case studies, where the end users benefited from the experience of a collaboration to address potential risks and improve plant reliability against metal dusting corrosion damage.