
Industrial demand for sulphur dioxide
Beyond its use in the manufacture of sulphuric acid, sulphur dioxide also has many industrial uses, especially in the food, paper, pharmaceutical and refining industries.

Beyond its use in the manufacture of sulphuric acid, sulphur dioxide also has many industrial uses, especially in the food, paper, pharmaceutical and refining industries.

A report on CRU’s annual Sulphur+Sulphuric Acid Conference, held in Barcelona, in early November.
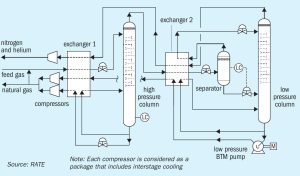
As the oil and gas industry focus on new requirements for CO2 recovery, cryogenic processes come under the spotlight. Mahin Rameshni and Stephen Santo of RATE USA discuss the importance of cryogenic processes in acid gas sweetening. Liquefied H2 S and CO2 reinjection is proposed as a cost effective alternative to large sulphur plants.

For six decades, Chemetics has been a pioneering force in the sulphuric acid design and equipment industry, consistently introducing groundbreaking technologies that have revolutionised the field by optimising the methodology in which chemicals are produced. This year, Chemetics celebrates its 60-year anniversary as one of the leading designers, direct equipment suppliers and fabricators that has modernised the sulphuric acid industry of today. This article dives into Chemetics’ rich history and key innovations that have shaped and moulded the industry.

In this revamp case study Scott Kafesjian and Quinn Kotter of Wood demonstrate how Wood sulphur technology was implemented at a 46-year old refinery SRU to improve reliability, operability and performance to meet new requirements for increased flexibility and higher availability.

This year will be the 40th Sulphur – now Sulphur + Sulphuric Acid – Conference to be held. From its beginnings in Canada to this year’s meeting at the Hyatt Regency hotel in Barcelona, much has changed, but its mission – to be an essential annual forum for the global sulphur and acid community – remains the same.
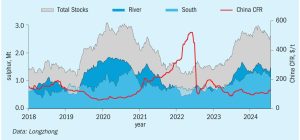
In the last two years there have been significant changes to the level and location of sulphur inventory, which has caused swings in short-term supply availability. Inventory plays a necessary role in balancing the sulphur market but exactly when, where, how, and why inventory enters the market can trigger a diverse range of price responses. In this insight article, CRU’s Peter Harrisson looks at how inventory change influences sulphur availability and pricing.
Join us at the CRU Sulphur + Sulphuric Acid 2024 Conference and Exhibition in Barcelona, 4-6 November, for a global gathering of the sulphur and sulphuric acid community. Meet leading market and technology experts and producers, network, share knowledge, and learn about market trends and the latest developments in operations, process technology and equipment.

Refinery sour water strippers are an often overlooked resource of low GWP ammonia. Martin A. Taylor and Charles L. Kimtantas of Bechtel Energy Technologies and Solutions, Inc. (BETS) show the results of a study on reusing an existing SWS as one of the major systems in a SWSPlus unit for the recovery of ammonia for sale. Relative cost factors will compare a complete SWSPlus unit versus reusing an existing SWS.

As more focus extends to a circular economy, there are industry wide discussions on whether future global sulphur demand will be challenged by the energy transition and decarbonisation. Hannes Storch, Collin Bartlett and Marcus Runkel of Metso discuss how the recycling of pyrite tailings could address some of these issues.