
Urea market developments
Urea markets are well supplied at present in spite of Chinese export restrictions, but face volatility due to a number of trade barriers and other non-market pressures.

Urea markets are well supplied at present in spite of Chinese export restrictions, but face volatility due to a number of trade barriers and other non-market pressures.

Global gas demand has returned to growth after the supply shock of 2022-23, but geopolitical tensions and short supply in LNG markets.
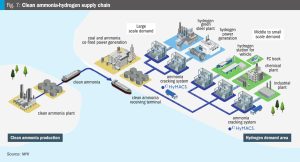
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries is developing a low temperature ammonia cracking technology (HyMACS™ ) that leverages exhaust heat from existing sources, such as boilers, steam turbines, engines, and heating furnaces. This innovative approach, which also includes the development of more efficient membrane separation technology using molecular sieves for hydrogen purification, is designed to offer a more sustainable, reliable and cost-effective pathway towards hydrogen production.

Common risks of ammonia cracking as a new technology and how these risks can be recognised and mitigated by applying an innovative approach of the technology maturation process is described as seen through the eyes of an end user/investor. Addressing those risks is pivotal to enable end users to choose the best technology for their needs. Albert Lanser of Duiker Clean Technologies discusses some of these risks and how they have been addressed in its novel technology for producing the lowest levelised cost of hydrogen via its unique ammonia cracking process.

NextChem compares KPIs and overall costs to evaluate the performance of several low carbon (blue) hydrogen production technologies. A detailed comparison of SCT-CPO, SMR and ATR technologies is reported.
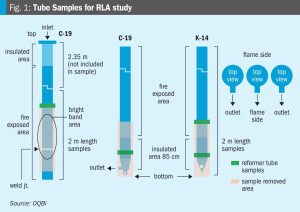
Muhammad Faisal Faraz and Abdullah Al Balushi of OQBi explain how by implementing a series of technical and process improvements, OQBi has successfully extended the lifespan of its reformer tubes by six years beyond the original design life of 100,000 hours.

To cope with higher demand for green and blue ammonia, new ammonia terminals will be required and must be designed with respect to social and environmental challenges, as well as local permitting regulations and safety requirements. Saipem has developed a wide range of solutions to tackle those challenges and requirements by offering large-scale liquid ammonia storage and import/export terminal facilities supported on gravity based structures.

While green hydrogen and green ammonia promise to be important clean energy carriers in future, there are significant challenges to be overcome not only in production storage and transport, but also financially realising the project. Innovate technology from thyssenkrupp Uhde, embodied in standardised, pre-integrated, modularised plant can deliver low cost of ownership and de-risks execution.

M.J. Cousins of Johnson Matthey and K. Nölker of thyssenkrupp Uhde discuss the integration of LCHTM technology and the uhde® ammonia process in providing low carbon ammonia at scale, efficiently, reliably and safely today.

Risk analysis tools such as hazard identification (HAZID), is often a first step in broader risk management and is especially valuable for green ammonia, where new technologies and processes introduce novel risks. This article explores various aspects of HAZID, from the basics of hazard identification to unique considerations specific to green ammonia facilities.