
Market Insight
Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media
The fertilizer industry’s ‘essential’ status is no barrier to bearish pricing, according to Andy Hemphill, senior markets editor for potash at ICIS Fertilizers.
We report on how the fertilizer industry and individual companies are working to mitigate the impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic.

Demand from horticulture has seen the use of water-soluble phosphates rise globally to almost one million tonnes annually. We assess the market and its growth prospects, identify leading producers and highlight recent product innovations.

The fertilizer market remains a commodity market. The three major nutrients N, P and K, more often than not, are supplied through four main products: urea, diammonium phosphate, monoammonium phosphate (DAP and MAP) and potassium chloride (MOP). Combined world consumption of these long-standing, globally-traded commodities is north of 300 million tonnes annually.

Weir Minerals has the global engineering expertise to tackle the world’s harshest and most extreme mine and quarry environments. These range from Canada’s frozen north to tropical Indonesia and the remote deserts of Chile, Mongolia and Australia. This expertise extends to Florida’s phosphate mining district, where a dedicated multi-disciplinary team is delivering an integrated approach to some tough mining challenges.
The phosphates market to date has remained remarkably resilient during the Covid-19 pandemic. Despite early fears, 2020 has seen strong overall demand so far and no major supply-side disruptions. But concerns still lie ahead, as Alberto Persona , principal phosphate analyst at Fertecon/IHS Markit, explains.

Following the publication of the 2020 nitrogen project listing by our sister magazine Nitrogen+Syngas, we profile a selection of leading nitrogen projects and their process licensors. Australia, Egypt, India, Nigeria and Russia have been key countries for new project developments.
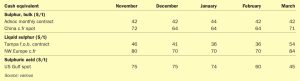
Meena Chauhan, Head of Sulphur and Sulphuric Acid Research, Argus Media, assesses price trends and the market outlook for sulphur.

Ordinarily I try to choose a different subject each issue for an editorial, but as April lengthens towards May, and here in the northern hemisphere we start to see the first signs of summer, there unfortunately remains only one subject that is obsessing every industry, and that is the Covid-19 pandemic and its impact upon every aspect of our lives. Since our last issue we have all had to come to terms with ‘lockdown’ and ‘social distancing’, as the grim toll of deaths climbs in all regions. Here at BCInsight we are working without an office as best we can, and issues of Sulphur will continue to land in your email inboxes, but paper copies of the magazines may take longer to arrive, if at all, as shipping and customs procedures are tightened all around the world, and I can only apologise and ask that you bear with us.