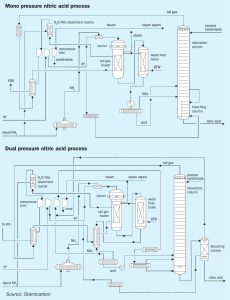
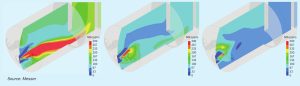
Catalyst management and monitoring in nitric acid plants
Based on 16 years of experience, Muhammad Nabeel Shakir of Fatima Fertilizer Company outlines a methodology to achieve optimum performance of the PGM catalyst and catchment system in nitric acid plants.