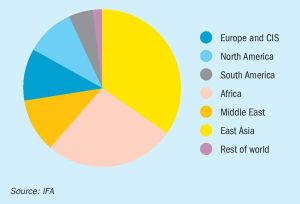
New phosphate demand – India and Brazil
The centre of gravity of the phosphate industry continues to shift, with Chinese exports less important, and fresh demand coming from India and Brazil.

The centre of gravity of the phosphate industry continues to shift, with Chinese exports less important, and fresh demand coming from India and Brazil.
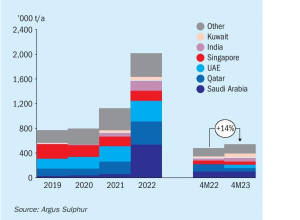
Meena Chauhan, Head of Sulphur and Sulphuric Acid Research, Argus Media, assesses price trends and the market outlook for sulphur.

Sulphur dust is one of the greatest hazards when producing and handling solid sulphur, and methods for its suppression are vitally important to prevent fire and explosion.

The modern sulphur industry is in effect a response to the environmental problems created by the presence of sulphur compounds in oil and gas, and the consequent release of sulphur dioxide when they are burned. The tens of millions of tonnes extracted, formed, traded and used for sulphuric acid production every year would otherwise be entering the atmosphere and causing health issues, especially in major cities, or returning as acid rain. One of the most recent step changes in sulphur recovery has come from the extension of rules on sulphur content of fuels that have been commonplace for road vehicles for many years into the maritime transport sphere. The International Maritime Organisation has mandated a reduction in sulphur content of bunker fuels to 0.5% worldwide, and 0.1% in busy shipping regions that have become designated emissions control areas (ECAs). Because bunker fuels were made from refinery residues, they often had high concentrations of sulphur in them; the limit before 2020 was 3.5%. As a result, a recent paper by two climate scientists calculates that global SO2 emissions have dropped by as much as 10% since 2020 because of the IMO limits. Given that atmospheric sulphur dioxide is responsible for an estimated 20-90,000 preventable deaths per year, this is surely a good thing.
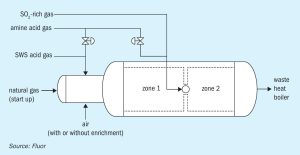
Fluor investigates how SO2 impacts the Claus furnace temperature in an SRU and the ways to mitigate it. This article studies the extent of quenching experienced in the Claus furnace with varying amounts of SO2 in the Claus feed. A case study is presented based on real operating data of a refinery Claus plant with a feed gas cocktail that includes substantial SO2 recovered from a regenerative flue gas desulphurisation unit.
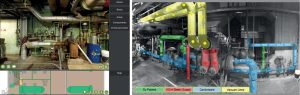
There is a growing skills gap in the sulphur industry due to the changing nature of the workforce. The traditional ways of doing things are no longer working effectively. Knowledge is lost with retiring subject matter experts (SMEs) and other experienced operations staff leaving a reducing pool of SMEs. In this article a case study reviews how knowledge automation solved the skills gap in a sulphur recovery unit at a major US refinery.

This June marks a milestone for this magazine; a platinum jubilee since the very first issue of the magazine was printed in 1953. It began life as the Quarterly Bulletin of the Sulphur Exploration Syndicate. The Syndicate was created in 1952, and was backed by nine major chemical producers, mainly in Britain and the US, who were concerned about dwindling world supplies of sulphur. Though some of these companies have vanished by the wayside over the years, including F.W. Berk and Co. Ltd, British Titan Products, Brotherton & Co., and Charles Tenant & Sons Ltd, others remain household names to this day, including Monsanto, Courtaulds (now part of Akzo-Nobel), and Dunlop (now owned by Goodyear), while Fisons’ fertilizer division was sold to Norsk Hydro in 1982 and today trades as part of Yara.

The recovery of waste heat from Aurubis’ copper smelting operation in Hamburg is already helping to reduce global carbon emissions and has the potential to provide heat for up to 20,000 homes through the district heating network in Hamburg’s HafenCity. The energy for the network comes from waste heat that Aurubis recovers from their sulphuric acid plant, using unique Alfa Laval plate heat exchanger technology.

Metso is launching an advanced sustainable battery black mass recycling process as part of its battery minerals technology offering, which covers concentration and hydrometallurgical processing as well as related services. Demand for battery minerals is increasing sharply with the ongoing transition to clean energy sources. An electric car battery weighs approximately 200 kg. Recycling of black mass from batteries with Metso’s process can reduce up to 60% of embedded carbon compared to use of virgin materials and enables the treatment of mechanically separated and shredded batteries for recovering battery raw materials like nickel, cobalt, and lithium, as well as manganese and copper.

BHP is committed to investing $5.7 billion to complete the first stage of the Jansen project and bring it into operation by the end of 2026. This under-construction Saskatchewan mine will then ramp up to produce more than four million tonnes of potash annually before the end of the decade.