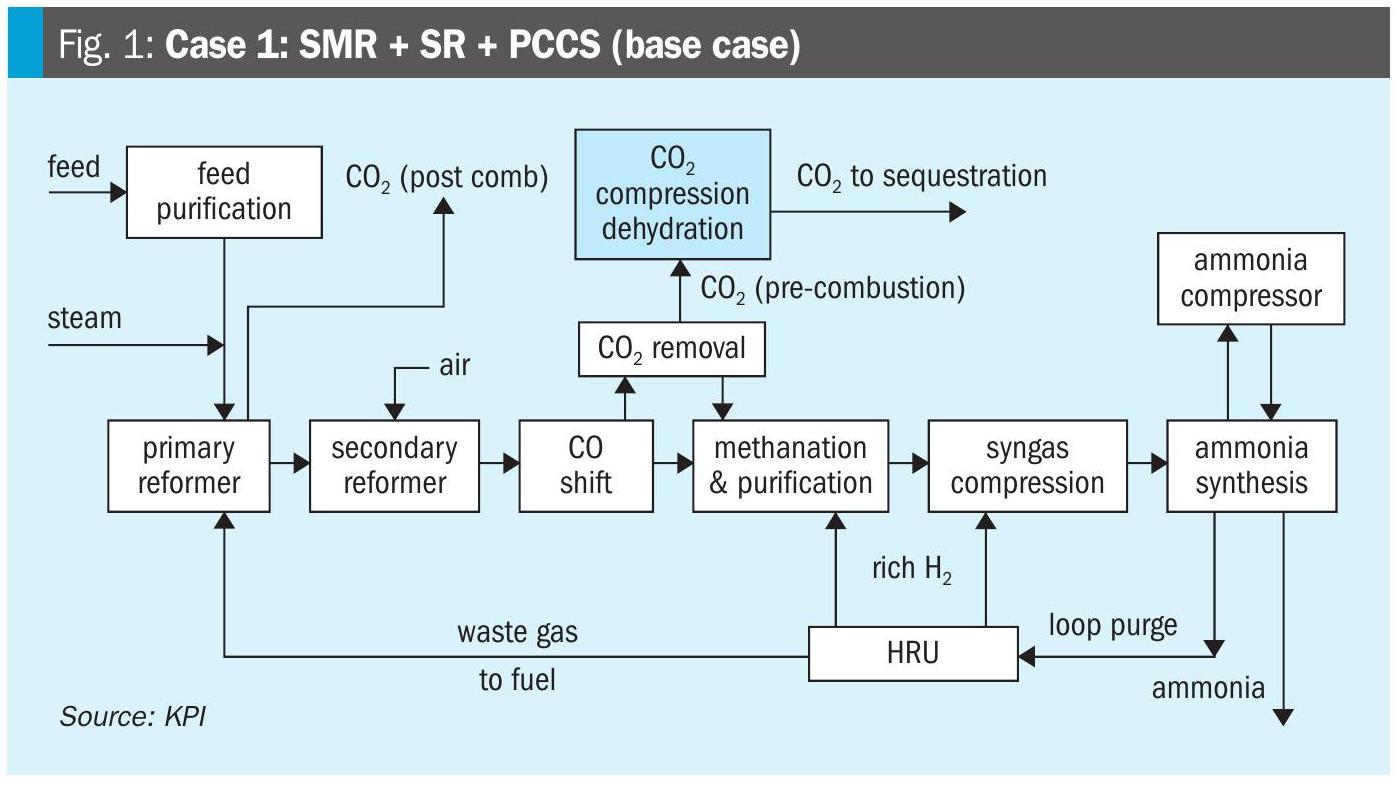
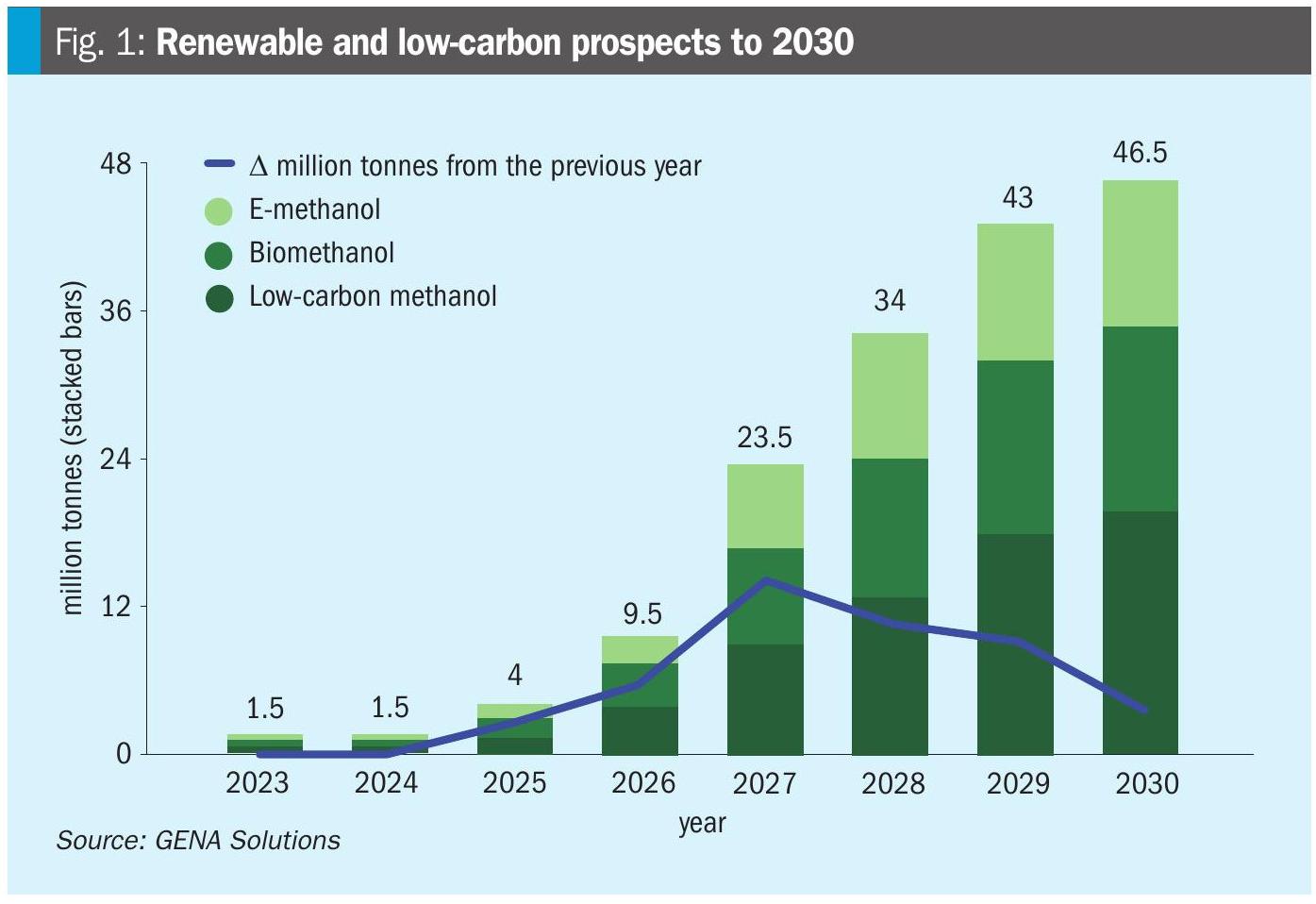
Nitrogen+Syngas 396 Jul-Aug 2025

21 July 2025
Hy2gen secures funding to accelerate Power-to-X projects
Renewable hydrogen producer Hy2gen AG has completed an additional funding round of €47 million from existing shareholders. The round was led by Hy24, via its Clean Hydrogen Infrastructure Fund, alongside engineering and technology company Technip Energies, and individual founding investor BenDa (the family fund of Hy2gen’s Chair Dana Kallasch). The capital will be used to accelerate the deployment of Hy2gen’s portfolio of projects producing renewable hydrogen and its derivatives in Europe, Canada and South America – to reach final investment decisions and prepare the construction phase. Hy2gen is designing, building, and operating green hydrogen, ammonia, SAF, e-methane and e-methanol plants using Power-to-X processes to support its clients in decarbonising energy-intensive and strategic ‘hard-to-abate’ sectors such as shipping and aviation, as well as chemicals and fertilizers. Hy2gen’s most advanced projects would represent a total installed electrolysis capacity of approximately 2 GW and a funding requirement of more than €5 billion to start the construction phase by 2027. These include the 300 MW Courant project in Canada, a renewable ammonia and ammonium nitrate plant of approximately €2 billion of capex, currently finalising its design, with construction expected to begin by 2027, the ‘Atlantis’ plant extension in Germany, which started producing renewable hydrogen in 2023, and the Iverson project in Norway, aiming to produce 200,000 t/a of renewable ammonia annually using renewable hydropower. In addition, Hy2gen is collaborating with H2V in the Fos-Marseille industrial basin, on a 390 MW project with a capex of approximately €1.5 billion, contributing to the decarbonization of Europe’s aviation sector with a production of 75,000 tons of sustainable aviation fuel.
Cyril Dufau-Sansot, CEO of Hy2gen, said: “Thanks to our financial and strategic investors we can take our projects to produce renewable hydrogen and hydrogen derivatives to the next level. Looking back at 2022, I am very pleased to receive another capital raise of €47 million thanks to our trusted investors. This enables us to establish ourselves as a top-tier supplier of renewable fuels to cut industrial emissions. With this continued support, we maintain our trajectory to lead the development of the renewable hydrogen industry. The demand for renewable hydrogen and hydrogen derivatives is growing with the long-term economic need to decarbonize industries.”
Pilot production plant for hydrogen electrolysers thyssenkrupp nucera and Fraunhofer IKTS have opened the first pilot production plant for high-temperature electrolysis (SOEC) stacks at Arnstadt, Thuringia. It follows a strategic cooperation agreement in March 2024 between the Fraunhofer research institute and nucera, a leading supplier of electrolysis technology for the production of green hydrogen. Building on the development work carried out by Fraunhofer IKTS, thyssenkrupp nucera will now work with Fraunhofer IKTS to advance SOEC technology for the manufacture of stacks for the production of green hydrogen on an industrial scale. The SOEC pilot plant initially produces stacks in small quantities and has a target production capacity of 8 MW per year.
SOEC stack technology is based on an oxygen-conducting ceramic electrolyte substrate with two electrodes, which are assembled together with coupling elements, the chromium-iron interconnectors, on several layers to form the stack. Chromium iron-based SOEC technology guarantees high corrosion resistance, optimized thermal cycle performance, and high long-term stability with regard to temperature cycling. In addition, stack technology requires only a small number of components and occupies a leading position compared to designs currently available on the global market. The SOEC cell design is also well-suited for highly automated series production. SOEC electrolysis leads to higher efficiency because less electrical energy is required to split water vapor at high temperatures. When commercial high-temperature electrolysis is used in processes that generate large amounts of waste heat, such as in the steel industry, electricity consumption can be reduced by 20% to 30% compared to other technologies.
“The outstanding properties of SOEC technology have prompted us to work with our strategic partner Fraunhofer IKTS to develop high-temperature electrolysis to market maturity. We are convinced of the advantages of this electrolysis technology for the production of green hydrogen. It will play a central role in a new, climate-friendly energy mix,” says Dr. Werner Ponikwar, CEO of thyssenkrupp nucera.