
Who’s who in fertilizer handling, bagging and blending
An update on the latest in fertilizer ship loading, handling, bagging and blending, including new contracts, company news and advances in technology.

An update on the latest in fertilizer ship loading, handling, bagging and blending, including new contracts, company news and advances in technology.

Major fertilizer industry players such as Stamicarbon, Nutrien and CF Industries are ramping up investment in ‘green’ and ‘blue’ fertilizer production. Consequently, low-carbon production technologies are being scaled-up and deployed commercially.

Maire Tecnimont SpA says that its subsidiaries MET Development, Stamicarbon and NextChem have collectively begun work on a renewable power-to-fertilizer plant in Kenya. MET Development has signed an agreement with Oserian Development Company for the development of the plant at the Oserian Two lakes Industrial Park, on the southern banks of Lake Naivasha, 100 km north of Nairobi.

Sulphur processing and handling equipment manufacturer IPCO has completed the commissioning of a groundbreaking new drum granulator in Italy that will serve as a global showcase for this patented system. C. Metheral of IPCO, describes the innovative approach and key features of the SG20 sulphur granulation system.

Filters can be a common bottleneck in overall plant operations. Jerold Johnson and Brad Bentley of WesTech outline how upstream modernisation or upgrades to the thickener can have significant benefits for the efficiency of filter operations downstream. Results are applicable to the dewatering of phosphate tailings and other fine particle tailings.

In August 2020 the tragic explosion of ammonium nitrate fertilizer in the port of Beirut caused many fatalities and injuries. This was a wake-up call for the entire industry to review the design of plants and storage facilities, as well as the procedures for plant operation and the handling of products. The key factor for safe new installations is the process design: the right choice of unit operations, operating temperatures and pressures, the control of process variables and the design of key items of equipment. A modern ammonium nitrate (AN) plant design not only mitigates the environmental impact, but also reduces investment costs and contributes to the key factors mentioned. M. Pieper and P. Kamermann of thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions discuss how, by using the right design, safety in ammonium nitrate plants can be easily achieved, while maintaining outstanding product quality.

Judging by the pages of the project announcements in our news section, you’d be forgiven for thinking that the ammonia and methanol industries were all running off hydrogen generated from electrolysis, and that we had already entered an era of ‘clean’ chemical generation which did not require fossil fuels as a feedstock. Of course, while companies can naturally be forgiven for wanting to put the best public face on their green credentials, it does obscure the fact that for the moment 99% of syngas generation comes from natural gas, coal, and some coke or naphtha.
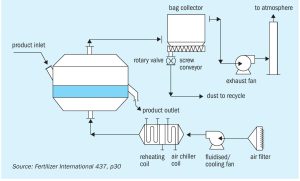
Plant operators require effective and efficient equipment for cooling the solid materials generated during fertilizer production. The main options include fluid bed coolers, rotary coolers and bulk flow coolers.

Automatic identification and optimum online monitoring using sonic velocity measurements can now be used to determine the concentration of both sulphuric acid and oleum.C. Kahrmann and T. Knape of SensoTech report on a new user-friendly method of measurement providing a significant step towards automated process control.

Ammonia synthesis catalysts have long lives and catalyst replacement is an infrequent activity. Many people will go through their careers in the ammonia industry without ever having to replace a synthesis catalyst and the infrequent nature of catalyst replacement means that many plants may not have direct experience of this activity. Ammonia synthesis catalyst can present a range of hazards throughout the replacement process, from transport through loading, reduction, start-up, shutdown and discharge, but the good practice illustrated in this article, and collaboration between catalyst suppliers and end users can ensure safe and successful catalyst changeouts.