
Who’s who in fertilizer handling, bagging and blending
An update on the latest in fertilizer ship loading, handling, bagging and blending, including new contracts, company news and advances in technology.

An update on the latest in fertilizer ship loading, handling, bagging and blending, including new contracts, company news and advances in technology.

Boron is a key micronutrient required by fruit and vegetables and crops such as corn, cotton, rice, soybean and sugar cane. The agricultural importance of boron and the wide range of products on the market are described.

OCI subsidiary Fertiglobe says that it has partnered with the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), to enable the sale by ADNOC of the first cargo of blue ammonia to Itochu in Japan, for use in fertilizer production. Fertiglobe, a 58% − 42% partnership between OCI and ADNOC respectively, will produce the blue ammonia at its Fertil plant at Ruwais in Abu Dhabi for delivery to ADNOC’s customers in Japan. This represent the first production milestone of a planned scale-up of blue ammonia production capabilities in Abu Dhabi, which is expected to include a low-cost debottlenecking program at Fertil. In addition, it was announced in June that Fertiglobe will join ADNOC and sovereign wealth fund ADQ as a partner in a new world-scale 1.0 million t/a blue ammonia project at Ta’Ziz in Ruwais, subject to regulatory approvals. The design contract for this project has been awarded, with a final investment decision expected in 2022 and start-up targeted for 2025. A feasibility study was also agreed in July betweenh the state-owned Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corp. (Jogmec), Inpex and JERA as well as ADNOC to explore the possibility of producing 1.0 million t/a of blue ammonia in Abu Dhabi and transporting it to Japan.
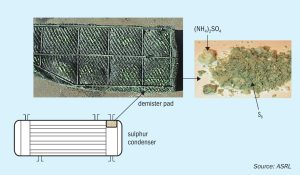
ASRL has conducted studies on ammonia destruction in the sulphur recovery unit (SRU) for over a decade1-5 . Other studies at ASRL have investigated mechanisms for ammonium salt formation and deposition downstream in the Claus plant, as well as the potential sources of ammonia (NH3 )in a gas plant7 . A less understood subject is addressing how much residual NH3 is tolerable or at what temperature will residual NH3 cause ammonium salt deposition. In this study, existing knowledge on thermal stability of ammonium salts and new measurements have been used to identify the gaseous components required for deposition, through reversible vapour pressure expressions.

Mining giant BHP’s decision this August to dispose of its oil and gas assets to Woodside Petroleum (see Industry News, page 11) in a deal estimated at $29 billion is certainly eye-catching. But it is also part of a larger pattern of divestment of fossil fuel assets by oil and gas companies who have dominated the industry for decades. It follows divestment by investors, institutional and otherwise, as efforts to tackle climate change consistently point towards a future where we will be using gas, and especially oil, far less – indeed, where many are talking about achieving ‘net zero’ carbon emissions by the middle of the century or shortly thereafter.

Corrosion is one of the most critical aspects regarding sulphuric acid plant lifespan. One important cause of corrosion in sulphuric acid plants is acid condensation from the process gas due to inadequate drying. E. Almeida, B. Ferraro, N. Clark, V. Machida and V. Sturm of Clark Solutions discuss this problem and how it can be avoided with proper tower and internals design.

John M. Bryant , President and CEO of The Sulphur Institute, looks at how the sulphur supply chain has reacted to the extraordinary circumstances of the pandemic over the past 18 months, and the key principles of a successful sulphur supply chain.

Ammonia and sulphur, as essential raw materials, underpin and drive fertilizer production costs. A steep and sustained rally has seen prices for both commodities reach new heights in recent months.

The delivery of nitrogen in nitrate form can deliver superior yields and quality in arable, fruit and vegetable crops. Because of this, production and consumption of the principal nitrate fertilizers – ammonium nitrate (AN), calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN), urea ammonium nitrate (UAN), potassium nitrate (NOP) and calcium nitrate (CN) – continue to grow.

Potassium nitrate is an efficient speciality fertilizer, being able to produce more for less. Whether applied to soils, via fertigation or through foliar application, it improves water use efficiency while boosting the uptake of potassium and other nutrients. Katja Hora and Harmen Tjalling Holwerda of SQM International highlight the main advantages of supplying potassium nitrate to crops.