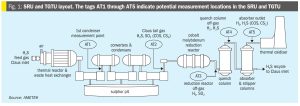
AMETEK Process Instruments has collaborated with Worley Comprimo, part of Worley’s Technology Solutions, to provide sulphur recovery unit (SRU) stakeholders with critical analytical measurements combined with advanced burner control technology to deliver enhanced automated air control management. The companies say that their 2ACT™ Solution is a fully automated system that minimises SRU upsets, enhances reliability, and delivers strong returns on investment. At the heart of this partnership, the innovative 2ACT™ Solution offers an all-in-one approach to advanced air control – significantly boosting SRU performance and efficiency while reducing operational costs. 2ACT uses AMETEK’s IPS-4 ultraviolet and infrared analyser to measure H2 S, CO2 , NH3 , H2 O and total hydrocarbons (THCs) by continuously sampling the acid gas upstream of the SRU. The change in air demand requirement is then calculated, with main and trim air adjustments implemented automatically by the feed forward control scheme designed by Worley Comprimo. The companies say that the benefits of the 2ACT Solution include maintaining an optimal H2S to SO2 ratio at the outlet of the Claus Plant to maximise recovery efficiency, mitigating damage to tail gas treatment unit (TGTU) components, lowering SO2 emissions and carbon footprint with improved uptime and plant throughput.