Syngas News Roundup
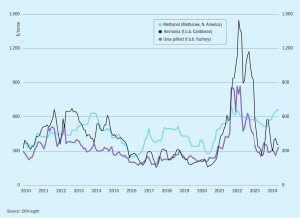
Methanex Corporation has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire OCI Global’s international methanol business for $2.05 billion. The transaction includes OCI’s interest in two world-scale methanol facilities in Beaumont, Texas, one of which also produces ammonia. The transaction also includes a low-carbon methanol production and marketing business and a currently idled methanol facility in the Netherlands.