Fertilizer Industry News Roundup
CF Industries has signed an agreement with thyssenkrupp to develop a commercial-scale green ammonia project at its Donaldsonville production complex in Louisiana.
CF Industries has signed an agreement with thyssenkrupp to develop a commercial-scale green ammonia project at its Donaldsonville production complex in Louisiana.
The Chemical & Process Technologies business unit of thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions is celebrating a milestone in 2021. It is one hundred years since engineer and entrepreneur Friedrich Uhde founded his own plant engineering company in a barn at his parents-in-law’s farm in Dortmund-Bövinghausen on April 6th, 1921. Now, in this centenary year, the origins of the firm are to become visible in its name again: thyssenkrupp is changing the business unit’s name to thyssenkrupp Uhde.

A recent report from BloombergNEF (New Energy Foundation) looking ahead to 2050 argues that green hydrogen can be cheaper than natural gas. It finds that ‘green’ hydrogen from renewables should become cheaper than natural gas (on an energy-equivalent basis) by 2050 in 15 of the 28 markets modelled, assuming scale-up continues. These countries accounted for one-third of global GDP in 2019. In all of the markets BNEF modelled, ‘green’ hydrogen should also become cheaper than both ‘blue’ hydrogen (from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage – CCS) and even ‘grey’ hydrogen from fossil fuels without CCS. The cost of producing ‘green’ hydrogen from renewable electricity should fall by up to 85% from today to 2050, the report predicts, leading to costs below $1/kg ($7.4/MMBtu) by 2050 in most markets. These costs are 13% lower than BNEF’s previous 2030 forecast and 17% lower than their previous 2050 forecast. Falling costs of solar photovoltaic (PV) electricity are the key driver behind the reduction; BNEF now believes that PV electricity will be 40% cheaper in 2050 than they had thought just two years ago, driven by more automatic manufacturing, less silicon and silver consumption, higher photovoltaic efficiency of solar cells, and greater yields using bifacial panels.
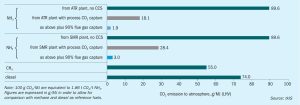
Reducing the carbon footprint in the synthesis of chemicals is a new global challenge as the world works towards providing sustainable products designed to minimise their environmental impacts throughout their whole lifecycle. This article looks at the role of blue technologies as part of a roadmap towards the decarbonisation of fuels and chemicals.
Because of the ongoing pandemic, this year’s CRU Nitrogen + Syngas conference was held as a ‘virtual’ event, in early March 2021.

Georgy Eliseev , Principal Analyst at Fertecon for IHS Markit, looks at the medium to long term outlook for both ‘green’ and ‘blue’ ammonia production.

The profound demand shock caused by Covid-related lockdowns has had a major impact upon the refining industry. Run rates have been at low levels in North America and Europe, and a new wave of rationalisation is under way, at the same time that capacity continues to grow in Asia. Will this spur diversification into petrochemicals and low carbon options for Atlantic basin refiners?

It can’t have escaped anyone’s notice that the question of the carbon intensity of ammonia and downstream nitrogen compound production has been one of the main industry talking points for the past year. Everyone seems to be talking about ammonia of different colours – green ammonia, blue ammonia, and all shades of turquoise in between. If you are confused, it may not be surprising, as these words have come to cover a wide variety of different methods and technologies for producing ammonia, and their green credentials consequently come in a whole range of different shades.

Johnson Matthey (JM) has secured a multiple licence for China’s Ningxia Baofeng Energy Group’s latest project to develop five of the largest single train methanol plants in the world. Located at Baofeng’s Ordos City complex in Inner Mongolia, the five plants each have a planned capacity 7,200 t/d. Under the agreement Johnson Matthey will be the licensor of all five plants and supplier of associated engineering, technical review, commissioning assistance, and catalyst. The plants will take synthesis gas as a feed and use JM radial steam raising converters in a patented series loop. Within the design, there is potential for 1-2% more feedstock efficiency over the life of the catalyst. Thanks to JM’s methanol loop synthesis technology, the plants will provide enhanced energy savings along with low OPEX, CAPEX and emissions. When complete, the plants will represent JM’s 13th operating license in China for a mega-scale plant (>5,500 t/d) and the fourth JM methanol design licensed by Ningxia Baofeng Energy.
Building on its long experience and leading position within global ammonia production, logistics and trade, Yara says that it aims to capture opportunities in green shipping, agriculture and industrial applications; a market expected to grow by 60% over the next two decades. A major first step includes plans to fully electrify its ammonia plant at Porsgrunn, Norway, with the potential to cut 800,000 t/a of CO 2 , equivalent to the emissions from 300,000 passenger cars.