
State-of-the-art plant technology
Saipem, Stamicarbon, Toyo Engineering Corporation and KBR showcase recent projects and latest technology for urea and nitric acid plants.

Saipem, Stamicarbon, Toyo Engineering Corporation and KBR showcase recent projects and latest technology for urea and nitric acid plants.

New innovations, services and latest technologies to improve the operation and reliability of steam methane reformers from AMETEK Land, Kontrolltechnik, BD Energy Systems, Koch Engineered Solutions, and Quest integrity.

Improvements to equipment and materials are driving greater operational performance and higher efficiencies at urea plants. Recent advances are reviewed.

Correct fertilizer usage at each crop stage can helps avocado growers improve their yield, quality and profitability. ICL’s Mateo Martinez and Alveiro Salamanca-Jimenez explain how growers can supply crop nutrients to avocado trees, efficiently and effectively, using economically- and environmentally-sustainable principles.

The ability to incorporate elemental sulphur within urea granules to create a fertilizer carrier has excellent potential as an answer to global soil sulphur deficiency. This technology is already available for commercial implementation and offers many benefits, as Bernd Peuckmann and Harald Franzrahe of thyssenkrupp Fertilizer Technology explain.
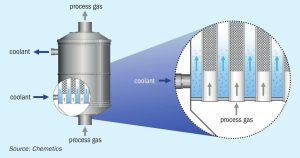
With climate change looming there is an increased focus on reducing the environmental footprint of the production of fertilizers. The use of renewable energy/green hydrogen is one way to make the fertilizer industry more environmentally sustainable. In this article, Rene Dijkstra of Chemetics introduces the Green Fertilizer Complex. This practical solution integrates an oxygen-based sulphuric acid plant using the Chemetics’ patented CORE-SO2™ process with a green hydrogen and ammonia facility to deliver low cost, low emission, and carbon-free phosphate (MAP/DAP) and/or sulphate (AMS) based ammonia fertilizers.

As all industries come under pressure to decarbonise, are there ways to reduce the carbon footprint of sulphur recovery operations?

A sulphuric acid plant forms critical material and energy interfaces with other plants in several different types of chemical and metallurgical complexes. Shailesh Sampat of SNC-Lavalin discusses how the acid plant design is customised to match the product mix and the energy requirements of the complex to provide the optimum solution for energy and material requirements.
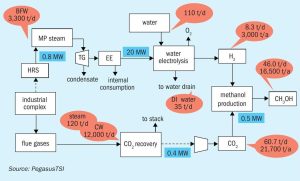
Ricardo L. Sepulveda of PegasusTSI reviews options to decrease the CO2 footprint of a fertilizer industrial complex and illustrates the technical and economic feasibility of utilising clean energy from a sulphuric acid plant in a fertilizer complex to produce green hydrogen, which in turn can be used to produce green methanol or green ammonia.
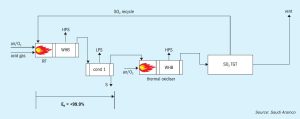
A new cost-effective alternative sulphur technology, providing a simple and robust process to achieve an overall sulphur recovery efficiency of 99.9+% is being developed by Saudi Aramco. J. P. O’Connell and I.A. Alami of Saudi Aramco discuss the new technology, its benefits and current stage of development.