
Lockdown lessons
The arrival of the Covid-19 pandemic has abruptly ended lives and livelihoods during its pernicious and inexorable spread across the globe. The fertilizer industry has not been immune to its parlous effects.

The arrival of the Covid-19 pandemic has abruptly ended lives and livelihoods during its pernicious and inexorable spread across the globe. The fertilizer industry has not been immune to its parlous effects.

Fertilizer International reached its 50th anniversary in 2019. The magazine’s continuing success is built on mutually beneficial partnerships forged over five decades. This year, we will continue to show our appreciation by profiling a much-valued commercial supporter in the magazine. This issue it’s the turn of the Lewis ® brand from Weir Minerals.
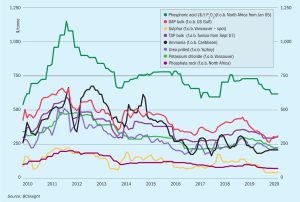
Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

A consortium of Chinese buyers has agreed the first potash contract with the Belarusian Potash Company (BPC) since September 2018.

CRU’s Laura Cross guides us through the current Covid-19 crisis and flags up the unique risks faced by the fertilizer industry as the pandemic unfolds.

Nutrien is the world’s largest crop nutrient company with a market capitalisation of almost $20 billion (Figure 1). This fertilizer industry giant produces and distributes over 25 million tonnes of potash, nitrogen and phosphate products for agricultural, industrial and feed customers globally. The company’s agriculture retail business also serves over 500,000 growers worldwide through a network of international outlets.

Three large-scale phosphoric acid plants constructed as part of the world-class Umm Wu’al project in Saudi Arabia are now fully operational. James Byrd of Worley (formerly Jacobs ECR) describes the execution of the project from basic engineering through to plant performance tests.
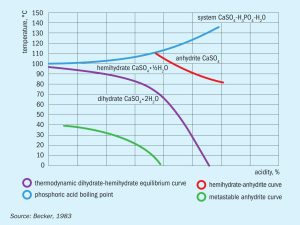
The DA-HF phosphoric acid process has been successfully implemented at Grupa Azoty’s Police fertilizer production plant in Poland, as part of a revamp of the site’s existing DH plant. Sébastien Havelange and Alexandre Wavreille of Prayon Technologies outline the performance improvements achieved by this first-of-its-kind plant.

We profile the US ‘big three’ North American phosphate producers, Mosaic, Nutrien and Simplot, and disruptive market entrant Itafos.
Nitrogen+Syngas’s annual listing of new ammonia, urea, nitric acid and ammonium nitrate plants shows that the key areas for new project developments are Egypt, India, Nigeria and Russia.