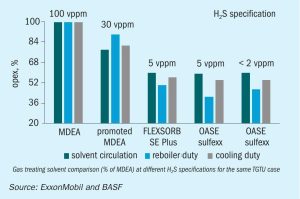
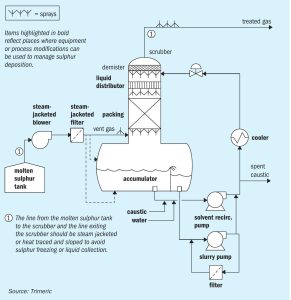
US crude production dropped rapidly during April and May, but figures released by the Energy Information Administration (EIA) showed that this had plateaued and there have been some well reactivations and drawdowns from crude stocks. Total production curtailments in North America were more than 2.5 million bbl/d in May. ConocoPhillips Chairman and CEO Ryan Lance said in remarks to the media that a return to pre-outbreak production levels of 13 million bbl/d looked “pretty difficult”, although a recovery to 11 million bbl/d or possibly as high as 12 million bbl/d would be possible, depending upon OPEC moves. About one third of the company’s production was shut in as of the start of June – some 400,000 bbl/d. Lance argued that low cost shale oil resources still exist in the US, but there will be pressure on companies to reduce capital spending. The Covid19 outbreak has had a major impact in investment announcements, with a large number of project delays in the US due to uncertainty over future demand levels. Planned US exploration and production expenditure is down by 50% for the second half of 2020, while the rig count was down 60% on February.