
Sulphur+Sulphuric Acid 2024
A report on CRU’s annual Sulphur+Sulphuric Acid Conference, held in Barcelona, in early November.

A report on CRU’s annual Sulphur+Sulphuric Acid Conference, held in Barcelona, in early November.
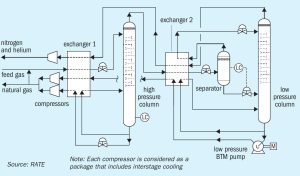
As the oil and gas industry focus on new requirements for CO2 recovery, cryogenic processes come under the spotlight. Mahin Rameshni and Stephen Santo of RATE USA discuss the importance of cryogenic processes in acid gas sweetening. Liquefied H2 S and CO2 reinjection is proposed as a cost effective alternative to large sulphur plants.

For six decades, Chemetics has been a pioneering force in the sulphuric acid design and equipment industry, consistently introducing groundbreaking technologies that have revolutionised the field by optimising the methodology in which chemicals are produced. This year, Chemetics celebrates its 60-year anniversary as one of the leading designers, direct equipment suppliers and fabricators that has modernised the sulphuric acid industry of today. This article dives into Chemetics’ rich history and key innovations that have shaped and moulded the industry.

In this revamp case study Scott Kafesjian and Quinn Kotter of Wood demonstrate how Wood sulphur technology was implemented at a 46-year old refinery SRU to improve reliability, operability and performance to meet new requirements for increased flexibility and higher availability.

OCP’s recent award of a contract to Worley Chemetics for three new greenfield sulphuric acid plants has confirmed the phosphate giant’s plans for its new Mzinda Phosphate Hub in Morocco, one of the largest investments in new phosphate capacity anywhere in the world over the next few years. It is part of a number of new investments under way in Morocco as OCP continues to expand its already considerable phosphate facilities. Three new fertilizer lines came onstream at Jorf Lasfar in 2023 and 2024, each with a capacity of 1 million t/a of diammonium phosphate (DAP). The Mzinda mega-project will add another 4 million t/a of triple superphosphate (TSP) capacity by around 2028-29, and will relieve some of the issues that OCP has in importing ammonia for DAP production, as TSP only requires phosphate rock and phosphoric acid. There is also an additional 1 million t/a of TSP capacity under construction at Jorf Lasfar, which is expected to be completed next year, and OCP also announced last year that it would build an integrated purified phosphoric acid (PPA) plant at Jorf Lasfar. The first phase of the project consists of 200,000 t/a of P2 O5 pretreated phosphoric acid capacity, 100,000 t/a (P2 O5 ) of PPA capacity, and 100,000 t/a of technical MAP (tMAP) capacity. The site will also be home to downstream production of phosphate salts and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) capacities. The initial plants will be delivered starting in mid-2026, carrying through into 2029, constructed in conjunction with JESA, a joint venture between OCP and Worley.
OCP Group has launched what it calls the Mzinda-Meskala Strategic Programme, aimed at significantly expanding fertilizer production in the country. Initially announced in December 2022, the program is set to enhance production capacity in two key regions: the Mzinda-Safi Corridor and the Meskala-Essaouira Corridor. This initiative is part of OCP’s broader strategy to meet growing global demand for fertilizers while committing to long-term sustainability goals, including achieving carbon neutrality by 2040.